Demographic, clinical, and laboratory features of Turkish patients with late onset ankylosing spondylitis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2015.511Keywords:
ankylosing spondylitis, late onset, features, TurkeyAbstract
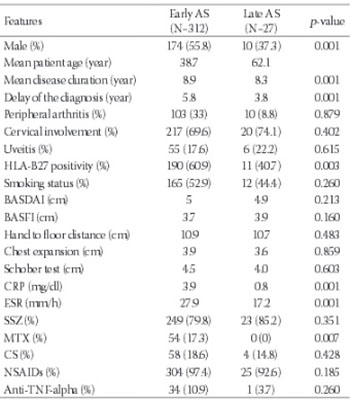
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disease, which typically begins in early decades of life with primarily axial joints involvement. This disease rarely affects patients older than 50 years of age. The aim of this study was to compare and evaluate the demographic, clinical, and laboratory features of late onset and early onset AS patients who were followed up in a single rheumatology center. A total of 339 patients who have been diagnosed with AS according to modified New York criteria were included in the study. The patients whose initial symptoms were observed after 50 years of age were accepted as late onset AS. Out of 339 patients, 27 (7.9%) were diagnosed as late onset AS and 312 (92.3%) patients were evaluated as early onset AS. Of 27 late onset patients, 10 were male and 17 were female. Delay in the diagnosis was 5.8 years for early onset AS, while it was 3.8 years for late onset AS (p = 0.001). Higher levels of acute phase reactants and more methotrexate (MTX) use were detected in early onset AS patients compared to late onset AS (p = 0.001, p = 0.007, respectively). Statistically, there was no difference between these two groups, with regard to disease clinical activity indexes, anthropometric measurement parameters, uveitis and peripheral joint involvement. In this study, we showed that early and late onset AS patients may present with different clinical, genetic, and laboratory features. Late onset AS patients are characterized with lower human leukocyte antigen-B27 sequence, less inflammatory sign, delayed diagnosis, and less MTX and anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha drug usage.
Downloads
References
Dougados M, van der Linden S, Juhlin R, Huitfeldt B, Amor B, Calin A, et al. The European spondylarthropathy study group preliminary criteria for the classification of spondylarthropathy. Arthritis Rheum 1991;34(10):1218-1227. http://www.dx.doi.org/10.1002/art.1780341003.
Braun J, Sieper J. Ankylosing spondylitis. Lancet 2007;369(9570):1379-1390. http://www.dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60635-7.
Lee W, Reveille JD, Davis JC Jr, Learch TJ, Ward MM, Weisman MH. Are there gender differences in severity of ankylosing spondylitis? Results from the PSOAS cohort. Ann Rheum Dis 2007;66(5):633-638. http://www.dx.doi.org/10.1136/ard.2006.060293.
Carbone LD, Cooper C, Michet CJ, Atkinson EJ, O'Fallon WM, Melton LJ rd. Ankylosing spondylitis in Rochester, Minnesota, 1935-1989. Is the epidemiology changing? Arthritis Rheum 1992;35(12):1476-1482. http://www.dx.doi.org/10.1002/art.1780351211.
Feldtkeller E, Bruckel J, Khan MA. Scientific contributions of ankylosing spondylitis patient advocacy groups. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2000;12(4):239-247. http://www.dx.doi.org/10.1097/00002281-200007000-00002.
Dubost JJ, Sauvezie B. Current aspects of inflammatory rheumatic diseases in elderly patients. Rev Rhum Mal Osteoartic 1992;59:37S-42S.
Toussirot E, Wendling D. Late-onset ankylosing spondylitis and related spondylarthropathies: clinical and radiological characteristics and pharmacological treatment options. Drugs Aging 2005;22(6):451-469. http://www.dx.doi.org/10.2165/00002512-200522060-00001.
Olivieri I, Pipitone N, D'Angelo S, Padula A, Salvarani C. Late-onset rheumatoid arthritis and late-onset spondyloarthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2009;27 (4 Suppl 55):S139-S145.
Olivieri I, Garcia-Porrua C, Padula A, Cantini F, Salvarani C, Gonzalez-Gay MA. Late onset undifferentiated spondylarthritis presenting with polymyalgia rheumatica feautures:description of seven cases. Rheumatol Int 2007;27(10):927-933. http://www.dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00296-007-0331-8.
Sezer I, Melikoglu MA, Cay HF, Kocabas H, Kacar C. A co-occurrence of sarcoidosis and ankylosing spondylitis: a case report. Rheumatol Int 2008;28(6):605-607. http://www.dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00296-007-0483-6.
Dubost JJ, Soubrier M, Ristori JM, Guillemot C, Bussière JL, Sauvezie B. Late-onset spondyloarthropathy mimicking reflex sympathetic dystrophy syndrome. Joint Bone Spine 2003;70(3):226-229. http://www.dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1297-319X(03)00041-1.
van der Linden S, Valkenburg HA, Cats A. Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum 1984;27(6):361-368. http://www.dx.doi.org/10.1002/art.1780270401.
Braun J, Pincus T. Mortality, course of disease and prognosis of patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2002;20 6 Suppl 28:S16-S22.
Davis JC, Dougados M, Braun J, Sieper J, van der Heijde D, van der Linden S. Definition of disease duration in ankylosing spondylitis: reassessing the concept. Ann Rheum Dis 2006;65(11):1518-1520. http://www.dx.doi.org/10.1136/ard.2005.044834.
Dubost JJ, Sauvezie B. Late onset peripheral spondyloarthropathy. J Rheumatol 1989;16(9):1214-1217.
Caplanne D, Tubach F, Le Parc JM. Late onset spondylarthropathy: clinical and biological comparison with early onset patients. Ann Rheum Dis 1997;56(3):176-179. http://www.dx.doi.org/10.1136/ard.56.3.176.
Olivieri I, Padula A, Pierro A, Favaro L, Oranges GS, Ferri S. Late onset undifferentiated seronegative spondyloarthropathy. J Rheumatol 1995;22(5):899-903.
Kay LJ, Walker DJ. Late onset spondyloarthropathy: Comparison with early onset patients. Ann Rheum Dis 1997;56(9):572. http://www.dx.doi.org/10.1136/ard.56.9.572.
Montilla C, Del Pino-Montes J, Collantes-Estevez E, Font P, Zarco P, Mulero J, et al. Clinical features of late-onset ankylosing spondylitis: Comparison with early-onset disease. J Rheumatol 2012;39(5):1008-1012. http://www.dx.doi.org/10.3899/jrheum.111082.
Feldtkeller E, Khan MA, van der Heijde D, van der Linden S, Braun J. Age at disease onset and diagnosis delay in HLA-B27 negative vs. positive patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatol Int 2003;23(2):61-66.
Chen HA, Chen CH, Liao HT, Lin YJ, Chen PC, Chen WS, et al. Clinical, functional, and radiographic differences among juvenile-onset, adult-onset, and late-onset ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol 2012;39(5):1013-1018. http://www.dx.doi.org/10.3899/jrheum.111031.
Toussirot E. Late-onset ankylosing spondylitis and spondylarthritis: an update on clinical manifestations, differential diagnosis and pharmacological therapies. Drugs Aging 2010;27(7):523-531. http://www.dx.doi.org/10.2165/11315970-000000000-00000.