Prognostic significance of survivin, β-catenin and p53 expression in urothelial carcinoma
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2015.556Keywords:
Survivin, β-catenin, p53, bladder, urothelial carcinoma, clinicopathologic valueAbstract
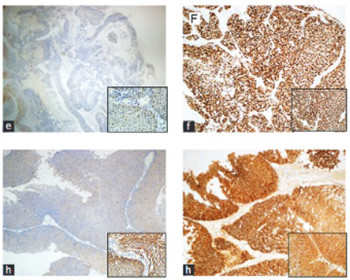
Survivin, β-catenin, and p53 are well-known cell-cycle and apoptosis regulators of tumorigenesis. Urothelial carcinomas (UCs) are the most common of the human cancers. Compared to superficial tumors (Ta, CIS, or T1), invasive UCs are important with regard to recurrence, progression, and mortality. Therefore, we examined whether survivin, β-catenin, and p53 could be used as the biomarkers for the early prediction of the invasiveness of UCs and the overall survival of the patients. We investigated the prognostic expressions of those biomarkers in UC (n=147) and in non-muscle invasive UC (NMI-UC) (n=113), using tissue microarray and immunohistochemistry. Spearman's correlation analysis and multivariate Cox regression analyses were used for statistical interpretation. High expressions of β-catenin, survivin, and p53 were associated with a high T stage, recurrence, progression, mortality, low recurrence-free survival, low progression-free survival and low overall survival (p < 0.01). Similar findings were achieved for recurrence and progression in the NMI-UC group, except for mortality. Moreover, a positive correlation was shown between p53 and β-catenin and between p53 and survivin (r=0.221, p < 0.01; r=0.236, p < 0.01, respectively). Survivin, p53, and β-catenin overexpression, as prognostic markers, might suggest that the UCs are biologically aggressive with the poor prognosis. Thus, dysregulation of those these cell-cycle and apoptosis regulators in bladder carcinoma could be used as a molecular marker to determine the best treatment strategy and could contribute to the development of targeted therapies.
Downloads
References
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 2012;62(1):10-29. doi: 10.3322/caac.20138.
Tadin T, Krpina K, Stifter S, Babarovic E, Fuckar Z, Jonjic N. Lower cyclooxygenase-2 expression is associated with recurrence of solitary non-muscle invasive bladder carcinoma. Diagn Pathol 2012;(5)7:152. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-7-152.
Fahmy M, Mansure JJ, Brimo F, Yafi FA, Segal R, Althunayan A, et al. Relevance of the mammalian target of rapamycin pathway in the prognosis of patients with high-risk non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Hum Pathol 2013;44(9):1766-1772. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2012.11.026.
Reed JC. Dysregulation of apoptosis in cancer. J Clin Oncol 1999;17(9):2941-2953.
Sah NK, Khan Z, Khan GJ, Bisen PS. Structural, functional and therapeutic biology of survivin. Cancer Lett 2006;244(2):164-171.
Kelly RJ, Lopez-Chavez A, Citrin D, Janik JE, Morris JC. Impacting tumor cell-fate by targeting the inhibitor of apoptosis protein survivin. Mol Cancer 2011;(6)10:35. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-10-35.
Kim PJ, Plescia J, Clevers H, Fearon ER, Altieri DC. Survivin and molecular pathogenesis of colorectal cancer. Lancet 2003;362(9379):205-209. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(03)13910-4.
Olie RA, Simoes-Wust AP, Baumann B, Leech SH, Fabbro D, Stahel RA, et al. A novel antisense oligonucleotide targeting survivin expression induces apoptosis and sensitizes lung cancer cells to chemotherapy. Cancer Res 2000;60(11):2805-2809.
Kostov M, Mijovic Z, Mihailovic D, Cerovic S, Stojanovic M, Jelic M. Correlation of cell cycle regulatory proteins (p53 and p16(ink)(4)(a)) and bcl-2 oncoprotein with mitotic index and thickness of primary cutaneous malignant melanoma. Bosn J Basic Med Sci 2010;10(4):276-281.
Shih HC, Shiozawa T, Miyamoto T, Kashima H, Feng YZ, Kurai M, et al. Immunohistochemical expression of E-cadherin and beta-catenin in the normal and malignant human endometrium: an inverse correlation between E-cadherin and nuclear beta-catenin expression. Anticancer Res 2004;24(6):3843-3850.
Urakami S, Shiina H, Enokida H, Kawakami T, Tokizane T, Ogishima T, et al. Epigenetic inactivation of Wnt inhibitory factor-1 plays an important role in bladder cancer through aberrant canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Clin Cancer Res 2006;12(2):383-391.doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1344.
Damalas A, Kahan S, Shtutman M, Ben-Ze'ev A, Oren M. Deregulated beta-catenin induces a p53- and ARF-dependent growth arrest and cooperates with Ras in transformation. Embo J 2001;20(17):4912-4922. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.17.4912.
Vousden KH, Prives C. Blinded by the Light: The Growing Complexity of p53. Cell 2009;137(3):413-431. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.04.037.
Shariat SF, Tokunaga H, Zhou J, Kim J, Ayala GE, Benedict WF, et al. p53, p21, pRB, and p16 expression predict clinical outcome in cystectomy with bladder cancer. J Clin Oncol 2004;22(6):1014-1024.doi:10.1200/JCO.2004.03.118.
Lu ML, Wikman F, Orntoft TF, Charytonowicz E, Rabbani F, Zhang Z, et al. Impact of alterations affecting the p53 pathway in bladder cancer on clinical outcome, assessed by conventional and array-based methods. Clin Cancer Res 2002;8(1):171-179.
Petitjean A, Achatz MI, Borresen-Dale AL, Hainaut P, Olivier M. TP53 mutations in human cancers: functional selection and impact on cancer prognosis and outcomes. Oncogene 2007;26(15):2157-2165.doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210302.
Wang Z, Fukuda S, Pelus LM. Survivin regulates the p53 tumor suppressor gene family. Oncogene 2004;23(49):8146-8153.doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1207992.
Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG, Greene FL, Trotti A. Urinary bladder, AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. New York: Springer; 2010.
Eble JN, Sauter G, Epstein JI, Sesterhenn IA. World Health Organization Classification of Tumours: Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs. Lyon: IARC Press; 2004.
Kitamura H, Torigoe T, Hirohashi Y, Asanuma H, Inoue R, Nishida S, et al. Nuclear, but not cytoplasmic, localization of survivin as a negative prognostic factor for survival in upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma. Virchows Arch 2013;462(1):101-107. doi: 10.1007/s00428-012-1343-7.
Li L, Fu X, Zhang W, Xiao L, Qiu Y, Peng Y, et al. Wnt signaling pathway is activated in right colon serrated polyps correlating to specific molecular form of beta-catenin. Hum Pathol 2013;44(6):1079-1088.doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2012.09.013.
Alvarez T, Miller E, Duska L, Oliva E. Molecular profile of grade 3 endometrioid endometrial carcinoma: is it a type I or type II endometrial carcinoma? Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36(5):753-761. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e318247b7bb.
Bongiovanni L, Mazzocchetti F, Malatesta D, Romanucci M, Ciccarelli A, Buracco P, et al. Immunohistochemical investigation of cell cycle and apoptosis regulators (survivin, beta-catenin, p53, caspase 3) in canine appendicular osteosarcoma. BMC Vet Res 2012;11(8):78.doi: 10.1186/1746-6148-8-78.
Yin W, Chen N, Zhang Y, Zeng H, Chen X, He Y, et al. Survivin nuclear labeling index: a superior biomarker in superficial urothelial carcinoma of human urinary bladder. Mod Pathol 2006;19(11):1487-1497.doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800675.
Waligorska-Stachura J, Jankowska A, Wasko R, Liebert W, Biczysko M, Czarnywojtek A, et al. Survivin--prognostic tumor biomarker in human neoplasms--review. Ginekol Pol 2012;83(7):537-540.
Mirza A, McGuirk M, Hockenberry TN, Wu Q, Ashar H, Black S, et al. Human survivin is negatively regulated by wild-type p53 and participates in p53-dependent apoptotic pathway. Oncogene 2002;21(17):2613-2622.doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205353.
Llopis J, Alcaraz A, Ribal MJ, Sole M, Ventura PJ, Barranco MA, et al.: p53 expression predicts progression and poor survival in T1 bladder tumours. Eur Urol 2000;37(6):644-653.doi:10.1159/000020232.
Malats N, Bustos A, Nascimento CM, Fernandez F, Rivas M, Puente D, et al. P53 as a prognostic marker for bladder cancer: a meta-analysis and review. Lancet Oncol 2005;6(9):678-686.doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(05)70315-6.
Lianes P, Charytonowicz E, Cordon-Cardo C, Fradet Y, Grossman HB, Hemstreet GP, et al. Biomarker study of primary nonmetastatic versus metastatic invasive bladder cancer. National Cancer Institute Bladder Tumor Marker Network. Clin Cancer Res 1998;4(5):1267-1271.
MacDonald BT, Tamai K, He X. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: components, mechanisms, and diseases. Dev Cell 2009;17(1):9-26. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2009.06.016.
Mann B, Gelos M, Siedow A, Hanski ML, Gratchev A, Ilyas M, et al. Target genes of beta-catenin-T cell-factor/lymphoid-enhancer-factor signaling in human colorectal carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1999;96(4):1603-1608.doi:10.1073/pnas.96.4.1603.
Resnik E. beta-Catenin--one player, two games. Nat Genet 1997;16(1):9-11.doi:10.1038/ng0597-9.
Chang E, Donahue J, Smith A, Hornick J, Rao JN, Wang JY, et al. Loss of p53, rather than beta-catenin overexpression, induces survivin-mediated resistance to apoptosis in an esophageal cancer cell line. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2010;140(1):225-232.doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2009.11.038.