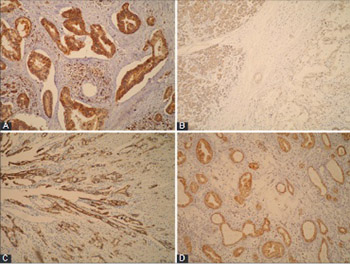
Immunohistochemical expression of NEDD9, E-cadherin and γ-catenin and their prognostic significance in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2018.2378Keywords:
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, PDAC, NEDD9, E-cadherin, γ-catenin, immunohistochemistryAbstract
Extensive research is being conducted to identify novel diagnostic, predictive and prognostic biomarkers for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), as only a few markers have been routinely used so far with limited success. Our aim was to assess the expression of neural precursor cell expressed developmentally down-regulated protein 9 (NEDD9), E-cadherin, and γ-catenin in PDAC in relation to clinicopathological parameters and patient survival. We also investigated if there is a correlation of NEDD9 expression with E-cadherin or γ-catenin. The protein expression was determined by immunohistochemistry in 61 PDAC and 61 samples of normal pancreatic tissue. The log rank test and Kaplan-Meier survival curve were used for survival analysis. E-cadherin and γ-catenin expressions were reduced in PDAC, and completely retained in normal pancreatic tissue. Expression of NEDD9 was significantly increased in PDAC (strong expression in 78.7% of cases and moderate in 21.3%) and reduced in normal pancreatic tissue (strong positivity in 45.9% of cases, moderate in 31.1%, and weak in 23%). There was a positive correlation between reduced E-cadherin and γ-catenin expression in PDAC (p = 0.015). The loss or reduced expression of E-cadherin had a negative impact on patient survival (p = 0.020). A negative correlation between E-cadherin expression and tumor grade was also observed (p = 0.011). Decreased E-cadherin expression was more common in male patients with PDAC (81.3% vs. 60% for females, p = 0.005). γ-catenin and NEDD9 expressions were not statistically correlated with tumor stage and grade, gender, nor with patient survival. Our results support the role of NEDD9, E-cadherin and γ-catenin proteins in PDAC, but further research should clarify in detail their mechanism of action in pancreatic cancer.
Downloads
References
Raimondi S, Maisonneuve P, Lowenfels AB. Epidemiology of pancreatic cancer: An overview. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2009;6(12):699-708. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2009.177.
Xue YZ, Sheng YY, Liu ZL, Wei ZQ, Cao HY, Wu YM, et al. Expression of NEDD9 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and its clinical significance. Tumour Biol 2013;34(2):895-9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-012-0624-8.
Law SF, Estojak J, Wang B, Mysliwiec T, Kruh G, Golemis EA. Human enhancer of filamentation 1, a novel p130cas-like docking protein, associates with focal adhesion kinase and induces pseudohyphal growth in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 1996;16(7):3327-37. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.16.7.3327.
Kim M, Gans JD, Nogueira C, Wang A, Paik JH, Feng B, et al. Comparative oncogenomics identifies NEDD9 as a melanoma metastasis gene. Cell 2006;125(7):1269-81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.06.008.
Ahn J, Sanz-Moreno V, Marshall CJ. Metastasis gene NEDD9 acts through integrin b3 and Src to promote mesenchymal motility and inhibit amoeboid motility. J Cell Sci 2012;125(7):1814-26. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.101444.
Weis WI, Nelson WJ. Re-solving the cadherin-catenin-actin conundrum. J Biol Chem 2006;281(47):35593-7. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.R600027200.
Drees F, Pokutta S, Yamada S, Nelson WJ, Weis WI. Alpha-catenin is a molecular switch that binds E-cadherin-beta-catenin and regulates actin-filament assembly. Cell 2005;123(5):903-15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2005.09.021.
Knudsen KA, Soler AP, Johnson KR, Wheelock MJ. Interaction of alpha-actinin with the cadherin/catenin cell-cell adhesion complex via alpha-catenin. J Cell Biol 1995;130(1):67-77. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.130.1.67.
Yin T, Getsios S, Caldelari R, Kowalczyk AP, Muller EJ, Jones JCR, et al. Plakoglobin suppresses keratinocyte motility through both cell-cell adhesion-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005;102(15):5420-5.
https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0501676102.
Todorovic V, Desai BV, Patterson MJ, Amargo EV, Dubash AD, Yin T, et al. Plakoglobin regulates cell motility through Rho- and fibronectin-dependent Src signaling. J Cell Sci 2010;123(20):3576-86. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.070391.
Hong SM, Li A, Olino K, Wolfgang CL, Herman JM, Schulick RD, et al. Loss of E-cadherin expression and outcome among patients with resectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Mod Pathol 2011;24(9):1237-47. https://doi.org/10.1038/modpathol.2011.74.
Shagisultanova E, Gaponova AV, Gabbasov R, Nicolas E, Golemis EA. Preclinical and clinical studies of the NEDD9 scaffold protein in cancer and other diseases. Gene 2015;567(1):1-11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2015.04.086.
Štajduhar E, Sedić M, Leniček T, Radulović P, Kerenji A, Krušlin B, et al. Expression of growth hormone receptor, plakoglobin and NEDD9 protein in association with tumour progression and metastasis in human breast cancer. Tumour Biol 2014;35(7):6425-34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-1827-y.
Natarajan M, Stewart JE, Golemis EA, Pugacheva EN, Alexandropoulos K, Cox BD, et al. HEF1 is necessary and specific downstream effector of FAK that promotes the migration of glioblastoma cells. Oncogene 2006;25(12):1721-32. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209199.
Sima N, Cheng X, Ye F, Ma D, Xie X, Lü W. The overexpression of scaffolding protein NEDD9 promotes migration and invasion in cervical cancer via thyrosine phosphorylated FAK and SRC. PlosOne 2013;8(9):e74594. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0074594.
Tikhmyanova N, Golemis EA. NEDD9 and BCAR1 negatively regulate E-cadherin membrane localization, and promote E-cadherin degradation. PLoS One 2011;6(7):e22102. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0022102.
Minn AJ, Gupta GP, Siegel PM, Bos PD, Shu W, Giri DD, et al. Genes that mediate breast cancer metastasis to lung. Nature 2005;436(7050):518-24. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03799.
Singh M, Cowell L, Seo S, O'Neill G, Golemis E. Molecular basis for HEF1/NEDD9/Cas-L action as a multifunctional coordinator of invasion, apoptosis and cell cycle. Cell Biochem Biophys 2007;48(1):54-72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-007-0036-3.
Nagathihalli NS, Mershant NB. Src-mediated regulation of E-cadherin and EMT in pancreatic cancer. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 2012;17:2059-69. https://doi.org/10.2741/4037.
Pećina-Šlaus N, Nikuseva Martić T, Deak AJ, Zeljko M, Hrasćan R, Tomas D, et al. Genetic and protein changes of E-cadherin in meningiomas. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2010;136(5):695-702. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-009-0708-z.
Pryczynicz A, Guzińska-Ustymowicz K, Kemona A, Czyzewska J. Expression of the E-cadherin-catenin complex in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Folia Histochem Cytobiol 2010;48(1):128-33. https://doi.org/10.2478/v10042-008-0089-1.
Takao S, Che X, Fukudome T, Natsugoe S, Ozawa M, Aikou T. Downregulation of E-cadherin by antisense oligonucleotide enhances basement membrane invasion of pancreatic carcinoma cells. Hum Cell 2000;13(1):15-20.
Von Burstin J, Eser S, Paul MC, Brandl M, Messer M, von Werder A, et al. E-cadherin regulates metastasis of pancreatic cancer in vivo and is suppressed by SNAIL/HDAC1/HDAC2 repressor complex. Gastroenterology 2009;137(1):361-71. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2009.04.004.
Lupu-Meiri M, Geras-Raaka E, Lupu R, Shapira H, Sandbank J, Segal L, et al. Knock-down of plasminogen-activator inhibitor-1 enhances expression of E-cadherin and promotes epithelial differentiation of human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells. J Cell Physiol 2012;227(11)3621-8. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.24068.
Hsu HP, Shan YS, Jin YT, Lai MD, Lin PW. Loss of E-cadherin and beta-catenin is correlated with poor prognosis of ampullary neoplasms. J Surg Oncol 2010;101(5):356-62. https://doi.org/10.1002/jso.21493.
Toyoda E, Doi R, Koizumi M, Kami K, Ito D, Mori T, et al. Analysis of E-, N-cadherin, alpha-, beta-, and gamma-catenin expression in human pancreatic carcinoma cell lines. Pancreas 2005;30(2):168-73. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.mpa.0000148514.69873.85.
Charpentier E, Lavker RM, Acquista E, Cowin P. Plakoglobin suppresses epithelial proliferation and hair growth in vivo. J Cell Biol 2000;149(2):503-20. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.149.2.503.
Kolligs FT, Kolligs B, Hajra KM, Hu G, Tani M, Cho KR, et al. Gamma-catenin is regulated by the APC tumor suppressor and its oncogenic activity is distinct from that of beta-catenin. Genes Dev 2000;14(11):1319-31. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.14.11.1319.