Cisplatin inhibits the proliferation of Saos-2 osteosarcoma cells via the miR-376c/TGFA pathway
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2020.4485Keywords:
Cisplatin, miR-376c, transforming growth factor alpha, TGFA, Saos-2, cell proliferation, cell growth, osteosarcomaAbstract
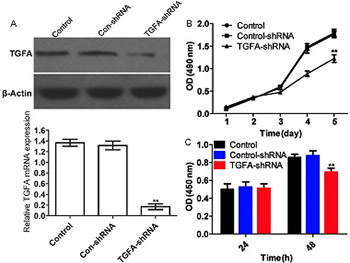
The transforming growth factor alpha (TGFA) gene is involved in the proliferation and metastasis of various tumors, but its role in cell sensitivity to cisplatin chemotherapy is unclear. In this study, we investigated the mechanism underlying inhibitory effects of cisplatin on growth and proliferation of osteosarcoma cells. Osteosarcoma and normal skeletal muscle tissues were collected from 26 patients by biopsy. TGFA was silenced or overexpressed in Saos-2 osteosarcoma cells by transfection with TGFA-shRNA or TGFA ORF clone, respectively. MiR-376c was inhibited or overexpressed by transfection of Saos-2 cells with miR-376c sponge or miR-376c mimics, respectively. Cell growth was analyzed by MTT assay and cell proliferation by BrdU assay. MiR-376c and TGFA mRNA expression was detected by quantitative reverse transcription PCR and TGFA protein expression by Western blot. The target relationship between miR-376c and TGFA was assessed by luciferase reporter assay. Both in osteosarcoma tissues and Saos-2 cells, miR-376c expression was significantly decreased and TGFA mRNA expression was significantly increased compared with control. Transfection of Saos-2 cells with TGFA-shRNA silenced TGFA expression and significantly inhibited cell growth and proliferation. TGFA mRNA and protein expression in Saos-2 cells significantly decreased with increasing cisplatin concentrations (2.5–10 mg/L). Transfection with TGFA ORF clone reversed the inhibitory effects of cisplatin on Saos-2 cell proliferation. Compared with cisplatin (10 mg/L) treatment alone, the combined treatment with cisplatin and miR-376c mimics inhibited the proliferation of Saos-2 cells more significantly. MiR-376c suppressed TGFA expression by directly interacting with its 3' UTR region. Overall, cisplatin inhibited the proliferation of Saos-2 cells by upregulating miR-376c and downregulating TGFA expression.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
How to Cite
Accepted 2019-12-06
Published 2021-04-01









