Mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow regulate invasion and drug resistance of multiple myeloma cells by secreting chemokine CXCL13
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2019.4344Keywords:
Mesenchymal stem cell, multiple myeloma, invasion, proliferation, CXCL13, CXCR5, MSC, U266, LP-1, chemokine, bortezomibAbstract
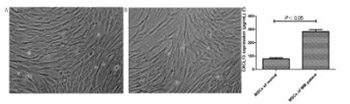
Multiple myeloma (MM) is a hematologic cancer arising from plasma cells. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are a heterogeneous cell population in the bone marrow microenvironment. In this study, we evaluated the regulatory effects of MSCs on the invasion and drug resistance of MM cells U266 and LP-1. Bone marrow samples from MM patients and healthy subjects were collected. MSCs were extracted from bone marrow and cultured, and their phenotypes were identified by flow cytometry. The level of CXCL13 in the supernatant of cultured MSCs was detected by ELISA. The protein expression of CXCR5 (a specific receptor of CXCL13) in U266 and LP-1 cells was detected by Western blot. The effects of MSCs on the invasion of U266 and LP-1 cells and the resistance to bortezomib were assessed by Transwell and CCK-8 assay, respectively. The mRNA and protein expressions of BTK, NF-κB, BCL-2, and MDR-1 were detected by RT-PCR and Western blot, respectively. CXCL13 was secreted by MSCs in the bone marrow microenvironment, and the level in MSCs from MM patients was significantly higher than that of healthy subjects. CXCR5 was expressed in both U266 and LP-1 cells. The resistance of MM cells to bortezomib was enhanced by MSCs through CXCL13 secretion. The invasion and proliferation of U266 and LP-1 cells were promoted, and the mRNA and protein expressions of BTK, NF-κB, BCL-2, and MDR-1 were upregulated by MSCs. The basic biological functions of MM cells U266 and LP-1 were affected by MSCs via the CXCL13-mediated signaling pathway. This study provides valuable experimental evidence for clinical MM therapy.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
How to Cite
Accepted 2019-08-08
Published 2020-05-01









