Lack of association between urotensin-II (UTS2) gene polymorphisms (Thr21Met and Ser89Asn) and migraine
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2017.2138Keywords:
Aura, migraine, urotensin-II, UTS2 gene, polymorphism, Thr21Met, Ser89AsnAbstract
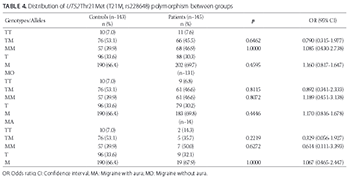
Migraine is a common neurovascular brain disorder with heterogeneous clinical presentation, including recurrent headache attacks. The pathophysiology of migraine is complex, and a number of genomic regions have been associated with the development of migraine. In this study, we analyzed the allele and genotype frequencies of the urotensin-II gene (UTS2) polymorphisms, Thr21Met and Ser89Asn, among Turkish patients with migraine. A total of 146 patients with migraine (14 with aura [MA group] and 132 without aura [MO group]) were genotyped for Thr21Met and Ser89Asn polymorphisms and compared with 154 age- and sex-matched healthy controls. The UTS2 gene polymorphisms were analyzed by polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP). No significant differences were observed in allele and genotype frequencies for Thr21Met and Ser89Asn polymorphisms between the patients with migraine and control group. Similarly, we did not observe significant differences in allele and genotype frequencies between MA and MO and control group. Moreover, the haplotype analysis showed no association between UTS2 gene haplotypes (MN, MS, TN, and TS) and migraine. In summary, Thr21Met and Ser89Asn polymorphisms of the UTS2 gene are not risk factors for migraine in our sample of Turkish migraine patients.
Citations
Downloads
References
Pietrobon D, Moskowitz MA. Pathophysiology of migraine. Annu Rev Physiol 2013;75:365-91. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-physiol-030212-183717.
Thomsen LL, Olesen J, Russell MB. Increased risk of migraine with typical aura in probands with familial hemiplegic migraine and their relatives. Eur J Neurol 2003;10(4):421-7. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1468-1331.2003.00621.x.
Stewart WF, Bigal ME, Kolodner K, Dowson A, Liberman JN, Lipton RB. Familial risk of migraine: Variation by proband age at onset and headache severity. Neurology 2006;66(3):344-8. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000196640.71600.00.
Headache Classification Subcommittee of the International Headache Society. The International Classification of Headache Disorders: 2nd edition. Cephalalgia 2004;24 Suppl 1:9-160. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-2982.2003.00825.x.
Peck KR, Johnson YL, Smitherman TA. Migraine. Handb Clin Neurol 2016;138:283-93. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-802973-2.00016-1.
Ozdemir G, Aygül R, Demir R, Ozel L, Ertekin A, Ulvi H. Migraine prevalence, disability, and sociodemographic properties in the eastern region of Turkey: A population-based door-to-door survey. Turk J Med Sci 2014;44(4):624-9.
https://doi.org/10.3906/sag-1307-4.
Mulder EJ, Van Baal C, Gaist D, Kallela M, Kaprio J, Svensson DA, et al. Genetic and environmental influences on migraine: A twin study across six countries. Twin Res 2003;6(5):422-31. https://doi.org/10.1375/136905203770326420.
Chasman DI, Schürks M, Anttila V, de Vries B, Schminke U, Launer LJ, et al. Genome-wide association study reveals three susceptibility loci for common migraine in the general population. Nat Genet 2011;43(7):695-8. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.856.
Ross B, McKendy K, Giaid A. Role of urotensin II in health and disease. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2010;298(5):R1156-72. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00706.2009.
Hongfang J, Bailin C, Bin Z, Chunyu Z, Xinmin L, Weijin Z, et al. Effects of hydrogen sulfide on hypoxic pulmonary vascular structural remodeling. Life Sci 2006;78(12):1299-309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2005.07.009.
Wenyi Z, Suzuki S, Hirai M, Hinokio Y, Tanizawa Y, Matsutani A, et al. Role of urotensin II gene in genetic susceptibility to Type 2 diabetes mellitus in Japanese subjects. Diabetologia 2003;46(7):972-6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-003-1145-1.
Anttila V, Winsvold BS, Gormley P, Kurth T, Bettella F, McMahon G, et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis identifies new susceptibility loci for migraine. Nat Genet 2013;45(8):912-7. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2676.
Geyik S, Ergun S, Kuzudişli S, Şensoy F, Temiz E, Altunışık E, et al. Plasma urotensin-2 level and Thr21Met but not Ser89Asn polymorphisms of the urotensin-2 gene are associated with migraines. J Headache Pain 2016;17:36. https://doi.org/10.1186/s10194-016-0623-z.
Kuzudisli SU, Yilmaz M, Gül Z, Demiryürek S, Yigiter R, Bozkurt H, et al. Investigation of the Rho-kinase 2 gene Thr431Asn polymorphism in migraine. Neurol India 2014;62(1):9-14. https://doi.org/10.4103/0028-3886.128241.
Okumus S, Igci YZ, Taskin T, Oztuzcu S, Gurler B, Eslik Z, et al. Association between Thr21Met and Ser89Asn polymorphisms of the urotensin-II (UTS2) gene, diabetes mellitus, and diabetic retinopathy. Curr Eye Res 2012;37(10):921-9. https://doi.org/10.3109/02713683.2012.688181.
Schürks M, Rist PM, Bigal ME, Buring JE, Lipton RB, Kurth T. Migraine and cardiovascular disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2009;339:b3914. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.b3914.
Vanmolkot FH, Van Bortel LM, de Hoon JN. Altered arterial function in migraine of recent onset. Neurology 2007;68(19):1563-70. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000260964.28393.ed.
Jiménez Caballero PE, Muñoz Escudero F. Peripheral endothelial function and arterial stiffness in patients with chronic migraine: A case-control study. J Headache Pain 2013;14(1):8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1129-2377-14-8.
Olesen J. The role of nitric oxide (NO) in migraine, tension-type headache and cluster headache. Pharmacol Ther 2008;120(2):157-71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2008.08.003.
Olesen J, Thomsen LL, Lassen LH, Olesen IJ. The nitric oxide hypothesis of migraine and other vascular headaches. Cephalalgia 1995;15(2):94-100.
https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1468-2982.1995.015002094.x.
Ross B, McKendy K, Giaid A. Role of urotensin II in health and disease. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2010;298(5):R1156-72. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00706.2009.
Bicak U, Karabiber H, Ozerol HI, Aslan M, Ilhan A, Yakinci C. Possible pathogenic link between migraine and urotensin-II. J Child Neurol 2008;23(11):1249-53. https://doi.org/10.1177/0883073808318052.
Chuquet J, Lecrux C, Chatenet D, Leprince J, Chazalviel L, Roussel S, et al. Effects of urotensin-II on cerebral blood flow and ischemia in anesthetized rats. Exp Neurol 2008;210(2):577-84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2007.12.004.
Ono T, Kawaguchi Y, Kudo M, Kushikata T, Hashiba E, Yoshida H, et al. Urotensin II evokes neurotransmitter release from rat cerebrocortical slices. Neurosci Lett 2008;440(3):275-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2008.05.096.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
How to Cite
Accepted 2017-06-01
Published 2017-08-20









