Artificial intelligence-assisted measurements of coronary computed tomography angiography parameters such as stenosis, flow reserve, and fat attenuation for predicting major adverse cardiac events in patients with coronary arterial disease
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2024.10497Keywords:
Coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA), artificial intelligence (AI), coronary artery disease (CAD), major adverse cardiac events (MACE)Abstract
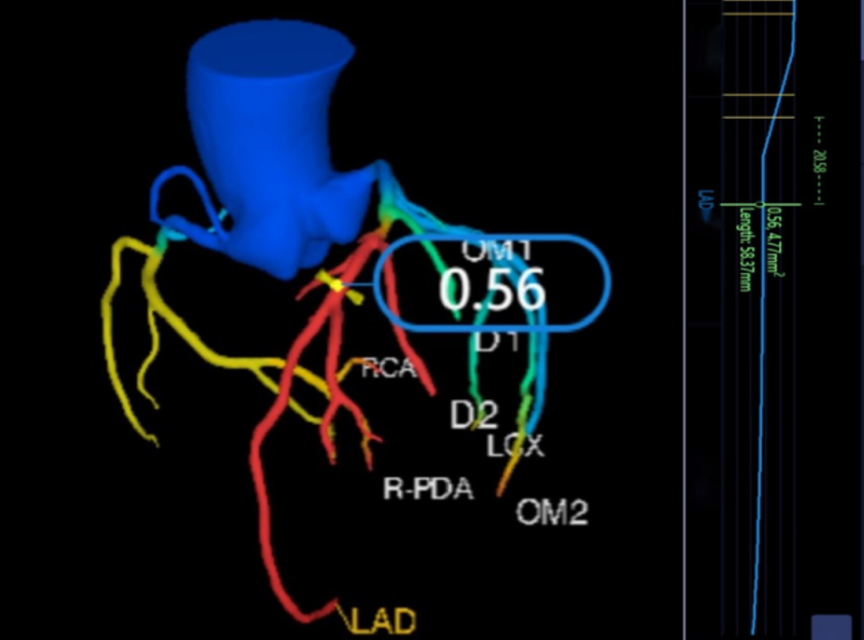
Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) offer promising tools for improving diagnostic accuracy and patient outcomes in cardiovascular medicine. This study explores the potential of AI-assisted measurements in enhancing the prediction of major adverse cardiac events (MACE) in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD). We conducted a retrospective cohort study involving patients diagnosed with CAD who underwent coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA). Participants were classified into MACE and non-MACE groups based on their clinical outcomes. Clinical characteristics and AI-assisted measurements of CCTA parameters, including CT-derived fractional flow reserve (CT-FFR) and fat attenuation index (FAI), were collected. Both univariate and multivariable logistic regression analyses were performed to identify independent predictors of MACE, which were used to build predictive models. Statistical analyses revealed three independent predictors of MACE: severe stenosis, CT-FFR ≤ 0.8, and mean FAI (P < 0.05). Seven predictive models incorporating various combinations of these predictors were developed. The model combining all three predictors demonstrated superior performance, as evidenced by the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.811 (95% confidence interval [CI] 0.774 – 0.847), a sensitivity of 0.776, and a specificity of 0.726. Our findings suggest that AI-assisted CCTA analysis, particularly using fractional flow reserve (FFR) and FAI, could significantly improve the prediction of MACE in patients with CAD, thereby potentially aiding clinical decision making.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Cheng Luo, Liang Mo, Zisan Zeng, Muliang Jiang, Bihong T. Chen

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









