Streptococcus anginosus: A new pathogen of superficial gastritis, atrophic gastritis and gastric cancer
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2024.10705Keywords:
Atrophic gastritis, gastric cancer, Helicobacter pylori, Streptococcus anginosus, superficial gastritisAbstract
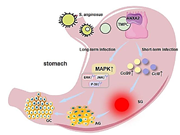
A wealth of research indicates that superficial gastritis (SG) and atrophic gastritis (AG) are precursors to gastric cancer (GC). While Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) has long been recognized as a key player in GC development, recent findings by Fu et al. have identified Streptococcus anginosus (S. anginosus) as an emerging pathogen that can trigger SG, AG and GC. S. anginosus, a gram-positive coccus, leverages its surface protein T. pallidum membrane protein C (TMPC) to engage with the annexin A2 (ANXA2) receptor of gastric epithelial cells, facilitating its colonization and invasion in the gastric mucosa. This leads to an upregulation of proinflammatory chemokines Ccl20 and Ccl8, causing prolonged effects on gastric barrier function and microbiota homeostasis, leading to SG. Moreover, these bacteria activate the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway, which is associated with the development of AG and GC. Importantly, inhibiting TMPC or knocking down ANXA2 can reduce S. anginosus colonization and invasion, lowering the chances of SG, AG, and GC. This paper highlights the molecular mechanisms of S. anginosus in SG, AG and GC, emphasizing the importance of a multi-pathogen strategy in gastric disease management and the need for further investigation into the role of S. anginosus in GC progression.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Fengting Guo, Lanfang Li, Lifang Li

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









