Efficacy and safety of CalliSpheres drug-eluting bead bronchial arterial infusion chemoembolization vs. bland embolization in advanced lung cancer with hemoptysis: A multicenter retrospective study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2024.10808Keywords:
Malignant lung tumors, massive hemoptysis, bronchial arterial infusion chemoembolization, drug-eluting bead embolization microspheresAbstract
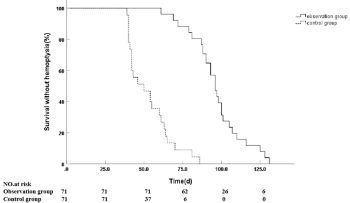
Massive hemoptysis is a life-threatening complication in patients with advanced primary lung cancer, and effective, safe treatments are crucial. This study aimed to investigate the efficacy and safety of CalliSpheres drug-eluting bead bronchial arterial infusion chemoembolization (DEB-BACE) for managing this condition. A retrospective analysis included 144 patients with advanced primary lung cancer and massive hemoptysis treated at multiple hospitals from January 2019 to January 2023. Patients undergoing bronchial artery embolization were divided into two groups: the observation group (n=76) received CalliSpheres DEB-BACE with epirubicin, and the control group (n=68) received 8spheres blank embolization. Both groups achieved successful hemostasis, with no statistically significant difference in success rates (observation group: 88.16%, control group: 86.76%). However, the observation group had a significantly longer median duration without hemoptysis (96 days vs. 50 days). Two months post-therapy, the observation group showed higher objective response rates (82.89% vs. 38.24%) and disease control rates (92.11% vs. 66.18%) compared to the control group. Adverse reactions were manageable and similar between groups, with no serious complications observed. By January 31, 2024, the observation group had significantly longer median overall survival (11 months vs. 7 months). The DEB-BACE treatment demonstrates safety and efficacy in managing massive hemoptysis in patients with advanced lung cancer. However, the superiority of this approach over bland embolization remains to be established through well-designed prospective studies. Future research is anticipated to provide a definitive comparison and further validate the role of DEB-BACE in clinical practice
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Song Liu, Maoli Yin, Song Liu, Huichao Xu, Guangji Yu, Xianchuang Liu, Guimin Chen, Weiwei Zhang

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









