Screening and validating genes associated with cuproptosis in systemic lupus erythematosus by expression profiling combined with machine learning
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2024.10996Keywords:
Systemic lupus erythematosus, machine learning, cuproptosis, single-cell RNA-sequencingAbstract
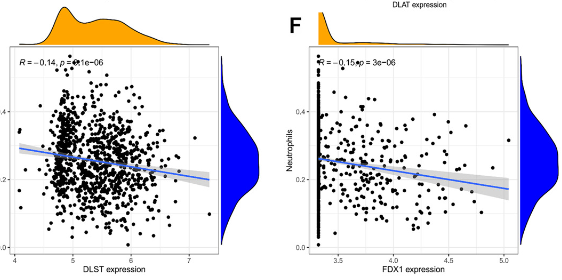
Cell death has long been a focal point in life sciences research, and recently, scientists have discovered a novel form of cell death induced by copper, termed cuproptosis. This paper aimed to identify genes associated with cuproptosis in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) through machine learning, combined with single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq), to screen and validate related genes. The analytical results were then experimentally verified. Two published microarray gene expression datasets (GSE65391 and GSE61635) from SLE and control peripheral blood samples were downloaded from the GEO database. The GSE65391 dataset was used as the training group, while the GSE61635 dataset served as the validation group. Differentially expressed genes from GSE65391 identified 12 differential genes. Nine diagnostic genes, considered potential biomarkers, were selected using the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator and support vector machine recursive feature elimination analysis. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves for both the training and validation groups were used to calculate the area under the curve to assess discriminatory properties. CIBERSORT was used to assess the relationship between these diagnostic genes and a reference set of infiltrating immune cells. scRNA-seq data (GSE162577) from SLE patients were also obtained from the GEO database and analyzed. Experimental validation of the most important SLE biomarkers was performed. Twelve significantly different cuproptosis-related genes were identified in the GSE65391 training set. Immune cell analysis revealed 12 immune cell types and identified nine signature genes, including PDHB, glutaminase (GLS), DLAT, LIAS, MTF1, DLST, DLD, LIPT1, and FDX1. In the GSE61635 validation set, seven genes were weakly expressed, and two genes were strongly expressed in the treatment group. According to the ROC curves, PDHB and GLS demonstrated significant diagnostic value. Additionally, correlation analysis was conducted on the nine characteristic genes in relation to immune infiltration. The distribution of key genes in immune cells was determined using scRNA-seq data. Finally, the mRNA expression of the nine diagnostic genes was validated using qPCR.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Zhongbin Xia, Shilu Liao, Ruoying Cheng, Qi Liu, Yuxin Zu

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









