KDM3A drives NSCLC proliferation and metastasis via H3K9 demethylation, EMT activation and MMP-9 upregulation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2025.11251Keywords:
Demethylation, non-small cell lung cancer, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, cell invasion, cell proliferation, KDM3AAbstract
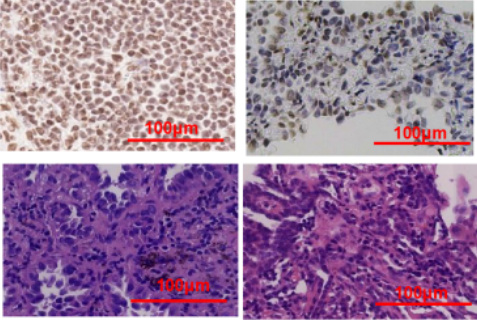
Histone methylation dysregulation is a crucial epigenetic driver of lung carcinogenesis; however, the role of lysine-specific demethylase 3A (KDM3A) in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) remains inadequately understood. In this study, we established NSCLC cell models with both KDM3A overexpression and knockdown to investigate its functional impact. In vitro assays demonstrated that KDM3A depletion increased histone H3 lysine 9 dimethylation (H3K9me2), suppressed cell proliferation, and impaired migration and invasion by attenuating epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9). Conversely, KDM3A overexpression led to reduced H3K9me2 levels, activated EMT, and enhanced metastatic potential. Mechanistically, KDM3A decreased H3K9me2 occupancy at the promoters of VIM and MMP-9, thus upregulating their expression. Additionally, KDM3A downregulated E-cadherin by activating the p-STAT3 pathway. In vivo, KDM3A knockdown significantly inhibited tumor growth in xenograft models. Clinical analyses revealed elevated KDM3A expression in metastatic NSCLC tissues, with a negative correlation between KDM3A and H3K9me2, and a positive association between KDM3A and FOXP3. These findings establish KDM3A as an epigenetic modulator of NSCLC progression through H3K9me2-dependent regulation of EMT and metastatic pathways, highlighting its therapeutic potential for NSCLC treatment.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Bingqing Shi, Zhe Wang, Lei Xiu, Luyao Li, Xiaolian Yang, Guanhua Wang, Jianjun Li, Hu Wang, Yuning Han

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









