Letrozole versus coenzyme Q10 plus Clomiphene citrate for women with Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome: An efficacy and safety analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2025.11386Keywords:
Clomiphene citrate, coenzyme Q10, letrozole, polycystic ovarian syndrome, PCOS, pregnancy, rotterdam criteriaAbstract
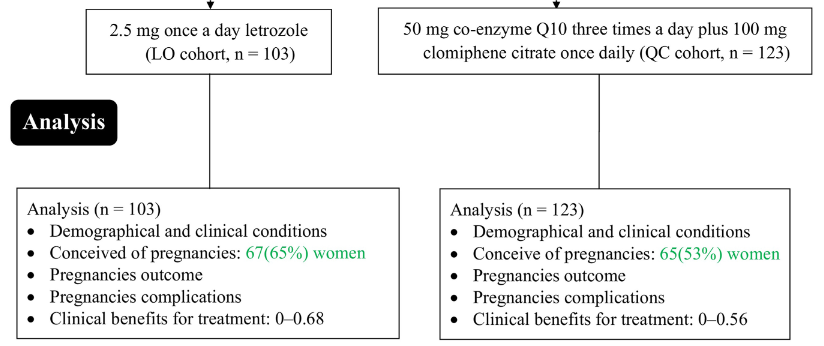
Clomiphene citrate is a well-established treatment for Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) but has poor efficacy and adverse effects. Coenzyme Q10 supplementation improves mitochondrial function. Letrozole has been reported to be effective with fewer adverse effects but is not approved for PCOS by the USFDA. This is a retrospective study in women diagnosed with PCOS to assess treatment with either 2.5 mg/day letrozole (LO cohort, n = 103) for 5 days per cycle (for 9 cycles). The QC group received additional doses of 50 mg coenzyme Q10 three times daily (QC cohort, n = 123). A third group received only 100 mg/day clomiphene citrate (CC cohort, n = 155) from the second day of the menstrual cycle for 5 days. After treatment, the duration of the menstrual cycle decreased across all cohorts (P < 0.001 for all), with a smaller reduction observed in the LTZ cohort compared to the QC and CC cohorts (P < 0.05 for all). The number of conceived pregnancies in the LTZ cohort (P < 0.0001) and the CC + QC cohort (P < 0.0001) was significantly higher than in the CC only group. Similarly, conception was higher in the CC + Q10 group than in the CC only group (P < 0.0001 for both groups). Letrozole versus clomiphene citrate plus coenzyme Q10 showed similar efficacy in achieving pregnancy in women with PCOS.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Juan Hou, Qingfen Chang

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









