Adipose-derived MSC extracellular vesicles ameliorate sepsis by reprogramming macrophages via miR-21-5p targeting PELI1
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2025.11971Keywords:
ADMSCs, extracellular vesicles, EVs, sepsis, macrophages, IL-10, miR-21-5pAbstract
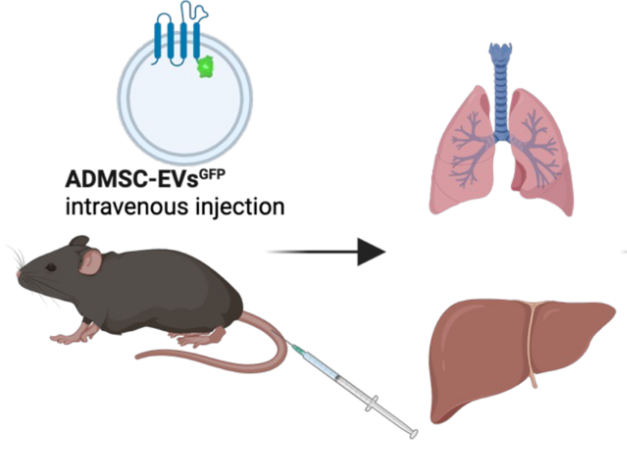
Sepsis is a common and life-threatening condition encountered in intensive care units (ICUs). Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) and their small extracellular vesicles (EVs) have emerged as promising nanotherapeutics, particularly in the context of COVID-19. This study evaluates the efficacy and mechanisms of adipose-derived MSC EVs (ADMSC-EVs) in a lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced sepsis model. We quantified M2 macrophages and IL-10 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from both septic patients and healthy donors. ADMSCs and their EVs were isolated, and EVs were administered to LPS-challenged mice. Macrophage phenotypes in lung tissue were analyzed using flow cytometry and immunofluorescence. The biodistribution of EVs was traced with PKH67 green fluorescent cell linker dye (PKH-67), and the signaling pathways involved in macrophage reprogramming were examined. ADMSC-EVs efficiently entered macrophages, promoted M2 polarization, suppressed inflammation, and improved survival rates in septic mice. Biodistribution studies demonstrated widespread organ accumulation, with notable localization in the lungs, liver, and kidneys. Mechanistically, the EV cargo miR-21-5p targeted Pellino E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1 (PELI1), driving M2 polarization in vivo, which was accompanied by increased IL-10 levels. These findings position ADMSC-EVs as a viable cell-free therapeutic approach for mitigating LPS-induced sepsis through the delivery of miR-21-5p to PELI1, thereby supporting further development of EV-based immunomodulatory strategies for sepsis management.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Guannan Zhou, Jieqiong Song, Lizhen Xuan, Zhunyong Gu, Yimei Liu, Cheng Xu, Hongyu He

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









