Integrative PANoptosis gene profiling reveals prognostic and therapeutic insights in prostate cancer
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2025.11998Keywords:
Gene risk signature, Prostate cancer, PCa, Programmed cell deathAbstract
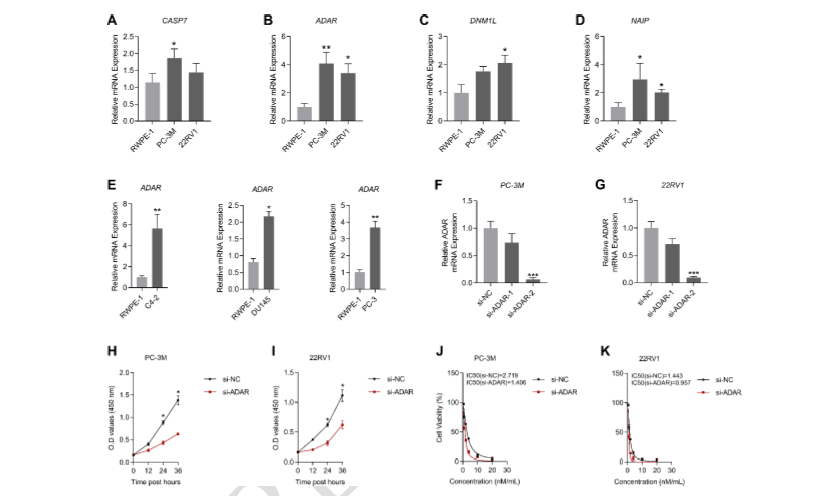
Prostate cancer (PCa) remains a significant global health challenge, representing the most common solid tumor in men and the fifth leading cause of cancer-related death. Despite therapeutic advances, achieving a definitive cure remains difficult. Early diagnosis and personalized treatment strategies are crucial for improving patient outcomes. Programmed cell death—particularly PANoptosis, an inflammatory pathway that integrates pyroptosis, apoptosis, and necroptosis—has emerged as a promising therapeutic target in oncology.In this study, individuals with PCa were categorized into PANoptosis-high and PANoptosis-low subgroups based on the expression levels of 45 PANoptosis-related genes. Differential gene expression analysis and subsequent enrichment analyses were conducted to explore the biological pathways associated with each subgroup. A four-gene risk signature (CASP7, ADAR, DNM1L, and NAIP) was identified, showing strong predictive value for overall survival (OS) in both training and validation cohorts. This signature was independently associated with OS and showed meaningful correlations with the tumor microenvironment, particularly immune cell infiltration and immunotherapy responsiveness. These findings suggest that the PANoptosis-related gene signature may serve as a valuable prognostic biomarker and inform immunotherapeutic strategies in PCa management.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Yi Wang, Yiheng Du, Xizhi Wang, Jiang Yu, Qing Gu, Guangquan Yuan, Yifei Zhu, Liyang Gu, Jun Ouyang

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









