Cutaneous inflammation alters nociceptor electrophysiology in guinea pigs but not rats
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2025.12195Keywords:
tissue inflammation, nociception, inflammatory pain, in vivo electrophysiology, nociceptorsAbstract
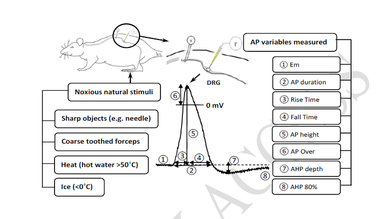
Inflammatory pain hypersensitivity is believed to result, in part, from increased excitability of nociceptive dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons. We previously demonstrated in guinea pigs that hindlimb inflammation induces electrophysiological changes in these neurons, including faster action potential (AP) and afterhyperpolarization (AHP) kinetics. Given that rats and guinea pigs are distinct species with notable differences in genetic composition and physiology, we hypothesized that cutaneous inflammation would have different effects on the electrophysiological properties of nociceptive DRG neurons in rats—the predominant rodent model for pain research. To test this hypothesis, we performed intracellular voltage recordings from DRG neurons (n = 430) in deeply anesthetized, untreated (control) and complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA)-treated rats and guinea pigs. C-, Aδ-, and Aβ-nociceptors were identified based on their dorsal root conduction velocities (CVs) and responses to natural noxious stimuli. Consistent with our hypothesis, we observed no significant changes in any electrophysiological variables in rat nociceptive neurons four days after CFA-induced hindlimb inflammation. In contrast, guinea pig nociceptors exhibited a significant increase in CV and significant decreases in both AP and AHP durations. The inflammation-induced shortening of absolute and relative refractory periods likely contributes to increased firing frequency in nociceptive nerve fibers, thereby promoting inflammatory pain hypersensitivity. These findings suggest species-specific differences in peripheral neuronal mechanisms underlying inflammatory pain, potentially due to variation in ion channel expression and/or function in DRG neurons between rats and guinea pigs. Given the genetic and metabolic similarities between guinea pigs and humans, further research is warranted to determine whether guinea pigs may serve as a more accurate model of chronic inflammatory pain than rats.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Laiche Djouhri , Ahmed Eliwa , Alghalya Al-Emadi , Yehia Y. Hussein , Hissa Al-Suwaidi , Al-Jouhara Albaloshi , Ayman Mustafa, Mohammed Seed Ahmed

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









