Low expression of CADPS predicts poor prognosis in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia without fusion genes
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2025.12254Keywords:
Pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia, ALL, fusion gene negative, FG-negative, next-generation sequencing, prognostic biomarkerAbstract
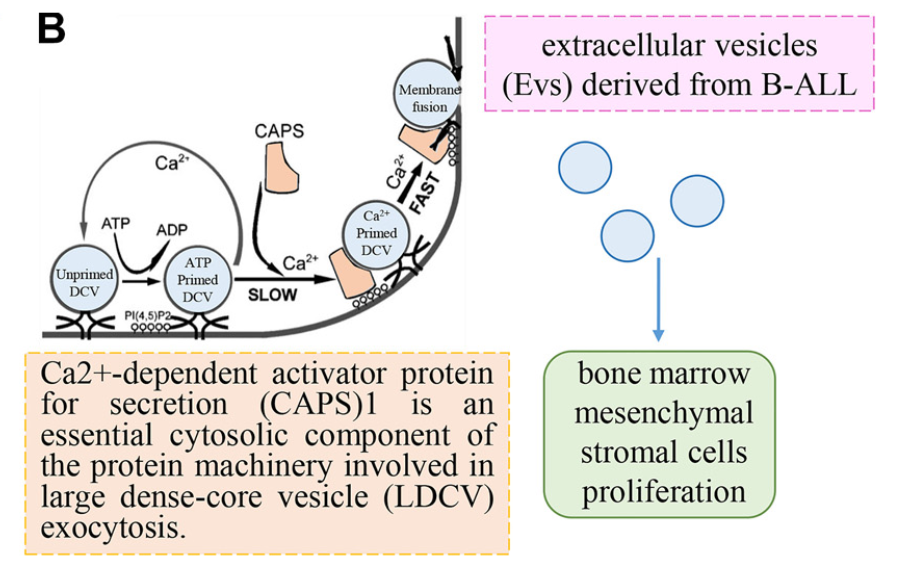
Pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is among the most prevalent hematological malignancies in children. Despite an overall cure rate approaching 90%, a subset of patients still experiences relapse, even with advanced therapeutic interventions. Research into the molecular characteristics and prognostic markers of fusion gene-negative (FG-negative) pediatric ALL remains limited. To address this gap, we performed whole-exome sequencing (WES) and whole-transcriptome sequencing (RNA-seq) on 54 FG-negative ALL cases from our center. Our results indicated that neither specific mutations nor tumor mutational burden significantly influenced relapse risk. Notably, we identified a significant downregulation of CADPS in FG-negative pediatric ALL patients who relapsed. The expression levels and prognostic significance of CADPS were further validated using data from the Therapeutically Applicable Research to Generate Effective Treatments (TARGET) cohort, where lower CADPS expression was associated with reduced event-free survival (EFS) and overall survival (OS) (P < 0.001 for both). Cox regression analyses were subsequently employed to identify OS-related factors and to construct a prognostic prediction model. Notably, this model demonstrated a significant correlation with therapeutic targets. In conclusion, our findings support the potential of CADPS expression as a novel biomarker for prognostic stratification in FG-negative pediatric ALL patients.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Bin Zhang, Chaoran Shi, Xiuxiu Wang, Jiajia Mi, Runan Wang, Shuang Li, Jiawei Yang, Qiuying He, Yujiao Wang, Zuofei Chi, Liangchun Hao

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









