Predictive value of inflammatory markers in inguinal hernia surgery: General vs. spinal anesthesia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2025.12262Keywords:
Inguinal hernia, anesthesia, lipopolysaccharide-binding protein, LBP, C-reactive protein, CRP, interleukin-6, IL-6, leukocytesAbstract
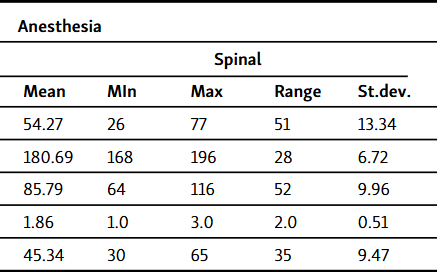
Inguinal hernia is a prevalent condition requiring surgical intervention, and accumulating evidence suggests that the type of anesthesia administered may influence systemic inflammatory responses. This study investigates the concentrations of inflammatory parameters in patients with inguinal hernia who underwent surgery utilizing either general or spinal anesthesia. The cohort comprised 87 male patients with inguinal hernia, classified as American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) physical status 1-2, who underwent elective surgical procedures. Participants were divided into two groups based on the anesthesia type: 44 received general anesthesia while 43 received spinal anesthesia. Plasma concentrations of leukocytes, C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and lipopolysaccharide-binding protein (LBP) were quantified using automated immunoassays and a hematological analyzer. Standard parametric and non-parametric statistical tests were employed for data analysis, and the predictive capacity of select parameters, along with body mass index (BMI) and age, was assessed through Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) analysis with Area Under the Curve (AUC). Statistical analysis via the t-test identified significant differences in LBP concentrations (LBP 1, LBP 2, and LBP 3) between patients receiving general and spinal anesthesia. Correlation analysis of BMI and the measured parameters revealed statistically significant positive correlations for LBP 1 and LBP 2 in patients who underwent spinal anesthesia. Notably, the preoperative concentration of LBP, with a cutoff value exceeding 9.7 µg/mL, suggests a potentially superior approach with spinal anesthesia compared to general anesthesia, demonstrating 50% sensitivity and 81.4% specificity. Other parameters did not exhibit statistical significance in differentiating the type of anesthesia used for inguinal hernia surgery.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Marko Kordić, Davorin Kozomara, Ivanka Mikulić, Vinka Mikulić, Martin Kajić, Miran Boras, Mateo Bevanda, Neven Soldo, Mijo Jović, Vedran Dragišić, Ines Rozić

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









