LncRNA interactomes and co-methylation in breast cancer regulation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2025.12333Keywords:
LncRNA PCR Array, lncRNAs co-expression, lncRNA genes co-methylation, ADAMTS9-AS2, lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory axesAbstract
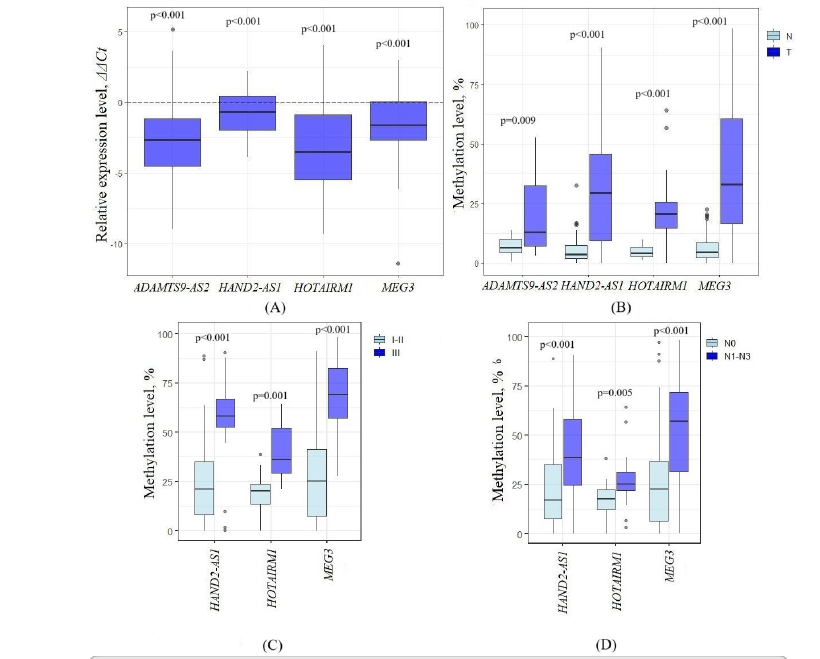
Breast cancer is the most commonly diagnosed malignancy in women. Despite advances in diagnostics and treatment, the key molecular mechanisms underlying its development remain incompletely understood. This study aimed to identify novel lncRNA–miRNA–mRNA regulatory networks potentially involved in breast cancer–associated signaling pathways. Using an RT² lncRNA PCR Array and bioinformatic analysis, we identified seven differentially expressed (DE) lncRNAs. Four of these—ADAMTS9-AS2, HAND2-AS1, HOTAIRM1, and MEG3—were prioritized through integrative evaluation. qPCR confirmed their downregulation and aberrant methylation in breast tumor samples. We observed significant positive expression correlations between the pairs ADAMTS9-AS2–MEG3, HAND2-AS1–MEG3, and HOTAIRM1–MEG3, as well as co-methylation among ADAMTS9-AS2–HAND2-AS1, ADAMTS9-AS2–HOTAIRM1, HAND2-AS1–MEG3, and HAND2-AS1–HOTAIRM1, suggesting coordinated regulation. These findings are consistent with data from GEPIA 2.0. Bioinformatic prediction identified TCF7L2 as a common target gene of these lncRNAs, which is involved in the Wnt, Hippo, and MAPK signaling pathways. We also identified several miRNAs interacting with ADAMTS9-AS2. In a cohort of 50 tumor samples, we confirmed inverse associations between ADAMTS9-AS2 expression and levels of miR-106a-5p (rs = –0.46, p = 0.03) and miR-17-5p (rs = –0.41, p = 0.04). Collectively, these findings reveal novel co-regulated lncRNA–miRNA axes and suggest their involvement in key signaling networks in breast cancer, providing a foundation for future functional studies and potential therapeutic targeting.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Elena A. Filippova, Irina V Pronina, Svetlana S Lukina, Alexey M Burdennyy, Tatiana P Kazubskaya, Vitaly I Loginov, Eleonora A Braga

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









