Deep learning predicts HER2 status in invasive breast cancer from multimodal ultrasound and MRI
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2025.12475Keywords:
Breast neoplasms, ERBB2 protein, human, ultrasound, US, magnetic resonance image, MRI, deep learning, DLAbstract
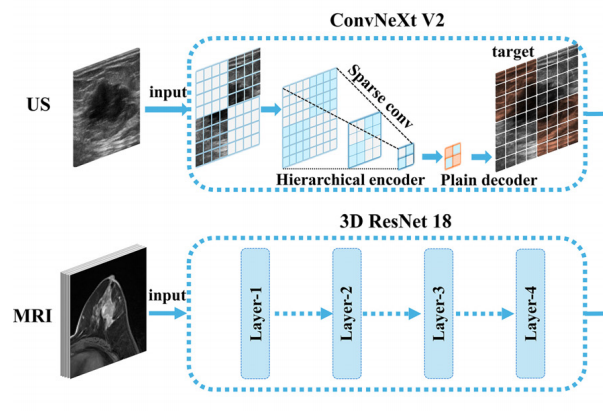
The preoperative human epidermal growth factor receptor type 2 (HER2) status of breast cancer is typically determined by pathological examination of a core needle biopsy, which influences the efficacy of neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC). However, the highly heterogeneous nature of breast cancer and the limitations of needle aspiration biopsy increase the instability of pathological evaluation. The aim of this study was to predict HER2 status in preoperative breast cancer using deep learning (DL) models based on ultrasound (US) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The study included women with invasive breast cancer who underwent US and MRI at our institution between January 2021 and July 2024. US images and dynamic contrast-enhanced T1-weighted MRI images were used to construct DL models (DL-US: the DL model based on US; DL-MRI: the model based on MRI; and DL-MRI&US: the combined model based on both MRI and US). All classifications were based on postoperative pathological evaluation. Receiver operating characteristic analysis and the DeLong test were used to compare the diagnostic performance of the DL models. In the test cohort, DL-US differentiated the HER2 status of breast cancer with an AUC of 0.842 (95% CI: 0.708–0.931), and sensitivity and specificity of 89.5% and 79.3%, respectively. DL-MRI achieved an AUC of 0.800 (95% CI: 0.660–0.902), with sensitivity and specificity of 78.9% and 79.3%, respectively. DL-MRI&US yielded an AUC of 0.898 (95% CI: 0.777–0.967), with sensitivity and specificity of 63.2% and 100.0%, respectively.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Yuhong Fan, Kaixiang Sun, Yao Xiao, Peng Zhong, Yun Meng, Yang Yang, Zhenwei Du, Jingqin Fang

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









