Vitamin D supplementation for tuberculosis prevention: A meta-analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2025.12527Keywords:
Tuberculosis, Prevention, Vitamin D, Supplementation, Meta-analysisAbstract
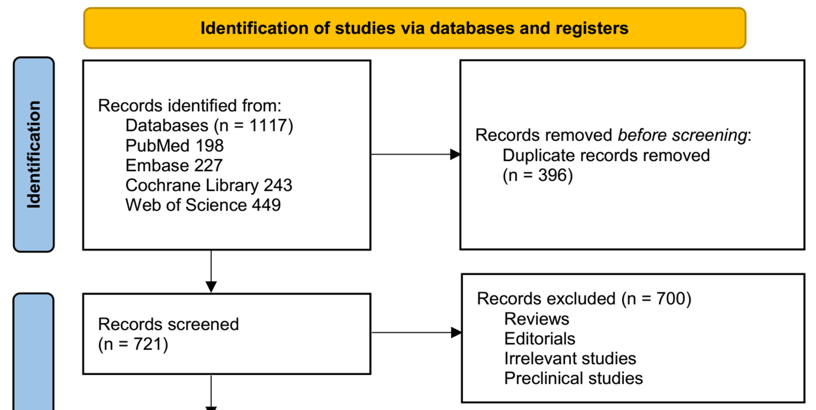
Vitamin D plays an important role in immune regulation, prompting interest in its potential for preventing tuberculosis. However, clinical findings regarding its protective effects against tuberculosis infection and disease remain inconsistent. We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to assess the impact of vitamin D supplementation on the prevention of tuberculosis infection and the progression to active tuberculosis. We searched PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science databases through January 2025. Eligible studies involved participants without active tuberculosis at baseline and reported outcomes related to tuberculosis. Pooled odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated using a random-effects model. Subgroup and sensitivity analyses were conducted, and the certainty of evidence was evaluated using the GRADE approach. Six RCTs, involving 15,677 participants, met our inclusion criteria. Compared to placebo, vitamin D supplementation did not significantly reduce the risk of tuberculosis infection (5 RCTs; OR: 0.95; 95% CI: 0.79–1.14; p = 0.55) or the development of active tuberculosis (4 RCTs; OR: 0.77; 95% CI: 0.56–1.05; p = 0.10). The certainty of evidence was moderate for both outcomes. Subgroup analyses based on baseline vitamin D levels and duration of follow-up yielded consistent results. The incidence of serious adverse events was comparable between the vitamin D and placebo groups (OR: 1.02; 95% CI: 0.76–1.38; p = 0.87), and none of the serious events were attributed to vitamin D supplementation. In conclusion, vitamin D supplementation does not significantly reduce the risk of tuberculosis infection or progression to active tuberculosis, although it is safe and well tolerated.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Sheng Liu, Tianyu Lin, Yanyu Pan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









