Development of a novel clinical prediction model for sepsis related mortality by combining NEWS, PIRO and lactate
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2025.12562Keywords:
Sepsis prognosis, risk assessment, intensive care unit, blood lactate levelsAbstract
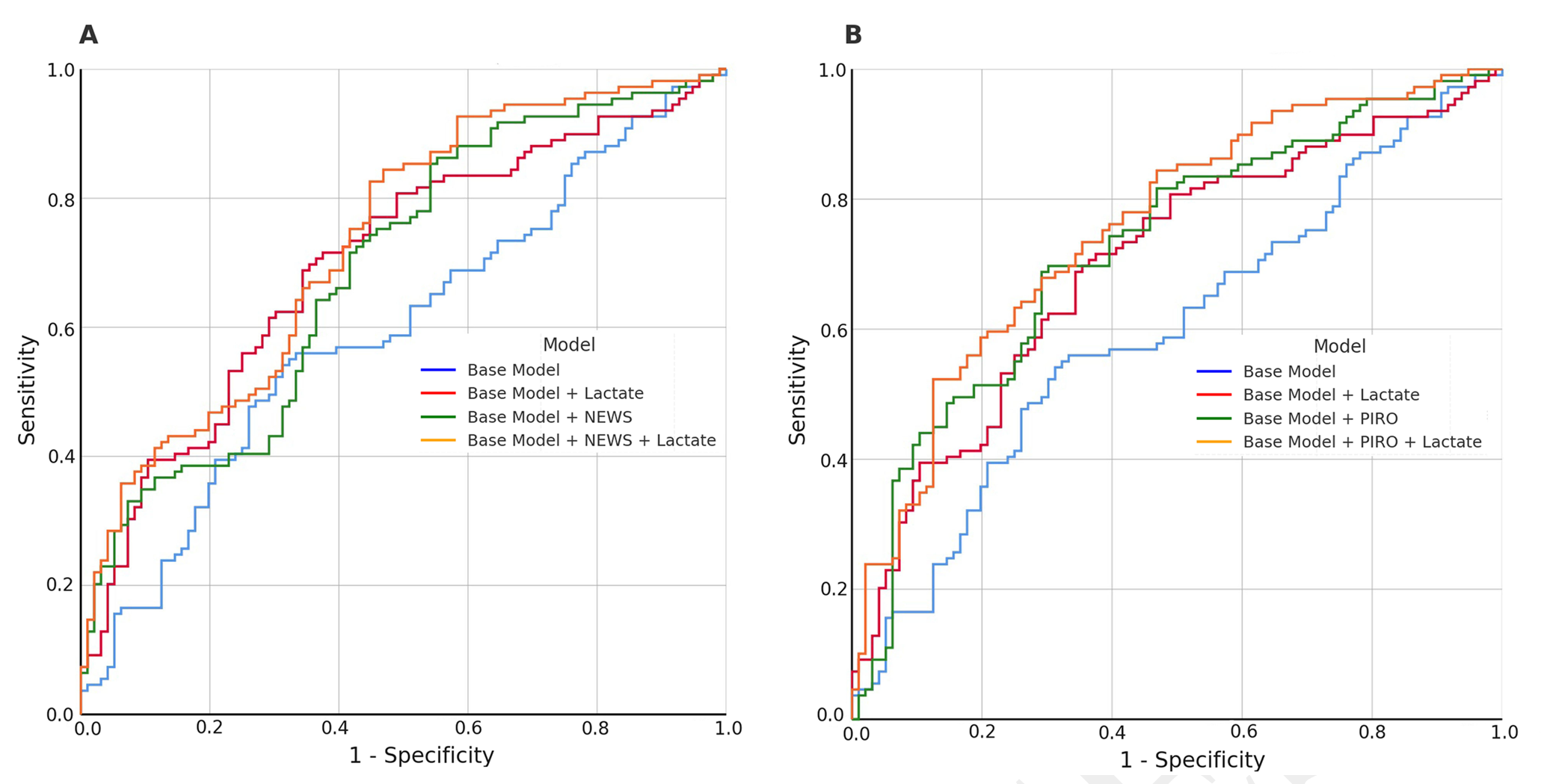
Prognostic assessment plays a crucial role in guiding therapeutic decision-making for patients with sepsis, particularly in intensive care settings. This study aimed to develop a multivariable model to predict 28-day mortality among intensive care unit (ICU) patients with sepsis by integrating serum lactate levels, the National Early Warning Score (NEWS), and the Predisposition, Infection, Response, and Organ Dysfunction (PIRO) score. Demographic information, clinical characteristics, and laboratory findings routinely collected at ICU admission were used to calculate the NEWS and PIRO scores for each patient. Patients were categorized as survivors or non-survivors based on their outcome. Both logistic regression and Cox proportional hazards models were applied for mortality prediction analysis. The final analysis included 205 patients diagnosed with sepsis (mean age: 73.6 ± 13.2 years; 53.2% male), of whom 109 died during hospitalization. Logistic regression analysis revealed that lactate, NEWS, and PIRO scores were independently associated with 28-day mortality. Combining lactate levels with NEWS and PIRO significantly enhanced mortality prediction, with the greatest accuracy observed when all three parameters were integrated. Pairwise analyses demonstrated that adding lactate to the base model significantly improved predictive accuracy (DBA: −0.103, p = 0.003), and incorporating lactate into a model already including NEWS further enhanced its predictive value (DBA: −0.042, p = 0.037). In conclusion, serum lactate measured at initial ICU admission provides valuable prognostic information for predicting 28-day mortality in sepsis patients. Furthermore, combining lactate levels with NEWS and PIRO scores substantially enhances the accuracy of mortality prediction in these patients.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Ozge Kurtkulagi, Ece Unal Cetin, Fatih Kamis, Murat Das, Esen Simsek, Ozgur Kurtkulagi, Adil Ugur Cetin, Yavuz Beyazit

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









