Response to the Letter regarding "Association between triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index and risk of depression in middle-aged and elderly Chinese adults: Evidence from a large national cohort study."
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2025.12760Keywords:
Triglyceride-glucose index, insulin resistant, depressive symptomAbstract
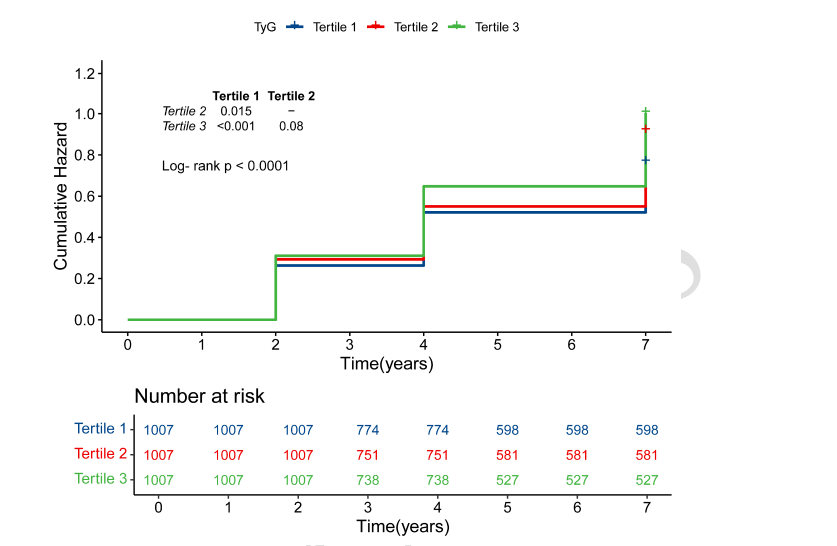
This response addresses constructive feedback on our CHARLS cohort study linking the triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index to depressive symptoms. As noted by the letter's author, a substantial body of research on TyG-related composite indices and mental disorders has emerged, with inconsistencies in cutoff values and the shape of dose-response curves observed among different indices. Our decision to focus solely on the single TyG index in this study was primarily motivated by the following two considerations. Firstly, the study population consisted of elderly individuals, among whom BMI levels cannot effectively reflect metabolic status. Secondly, this study represents a continuation of our group's preliminary preclinical research, thus specifically focusing on the factor of insulin resistance. Different findings derived from different indices necessitate consideration of various factors, including different application contexts, variations in the study populations, and differences in data processing methods. Finally, we believe more large randomized controlled trials and related pharmacological intervention studies are essential to validate the use of TyG and its related indices in the diagnosis and treatment of psychiatric disorders.
This is the response to Letter to the Editor which you can read here: https://www.bjbms.org/ojs/index.php/bjbms/article/view/12739.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Zhang-Yang Xu, Yun-Xia Wang, Wen-Jun Su

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









