Platelet-rich plasma and hyaluronic acid in the treatment of acute ankle sprains: A review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2025.13327Keywords:
Ankle injuries, platelet-rich plasma, hyaluronic acid, regenerative medicine, sprains and strainsAbstract
Ankle sprains are prevalent musculoskeletal injuries commonly encountered in the general population, particularly among athletes. While conventional treatments are widely practiced, regenerative therapies have emerged as potential adjunctive options. This narrative review aims to assess the role of regenerative therapy in the management of acute ankle sprains and evaluate its efficacy through an analysis of the literature. We focused on studies available in PubMed, restricting our search to English-language articles published between January 2005 and December 2024. Our review identified five studies on platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and one on hyaluronic acid (HA). The PRP studies included four clinical trials and one case report. PRP injections demonstrated short-term benefits in pain reduction and functional recovery, particularly when administered early and in multiple doses. However, long-term outcomes were often comparable to standard treatments or placebo. The study on HA indicated consistent and sustained advantages over placebo in alleviating pain, expediting the return to sport, and reducing recurrence rates. Based on the current evidence, PRP and HA may function as adjunctive therapies for acute ankle sprains, especially for short-term symptom relief and functional recovery. Treatment efficacy appears to be influenced by factors such as injection timing, volume, immobilization protocols, and the concurrent use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Nonetheless, the evidence base remains constrained by small sample sizes, heterogeneous protocols, and a lack of long-term follow-up. Therefore, further high-quality randomized controlled trials are essential to establish standardized protocols and ascertain the long-term efficacy of these regenerative therapies.
Citations
Downloads
References
Vuurberg G, Hoorntje A, Wink LM, van der Doelen BFW, van den Bekerom MP, Dekker R, et al. Diagnosis, treatment and prevention of ankle sprains: update of an evidence-based clinical guideline. Br J Sports Med 2018;52(15):956. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2017-098106.
Petersen W, Rembitzki IV, Koppenburg AG, Ellermann A, Liebau C, Brüggemann GP, et al. Treatment of acute ankle ligament injuries: a systematic review. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2013;133(8):1129-41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-013-1742-5.
Fong DT, Ha SC, Mok KM, Chan CW, Chan KM. Kinematics analysis of ankle inversion ligamentous sprain injuries in sports: five cases from televised tennis competitions. Am J Sports Med 2012;40(11):2627-32. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546512458259.
van Rijn RM, van Os AG, Bernsen RM, Luijsterburg PA, Koes BW, Bierma-Zeinstra SM. What is the clinical course of acute ankle sprains? A systematic literature review. Am J Med 2008;121(4):324-31.e6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2007.11.018.
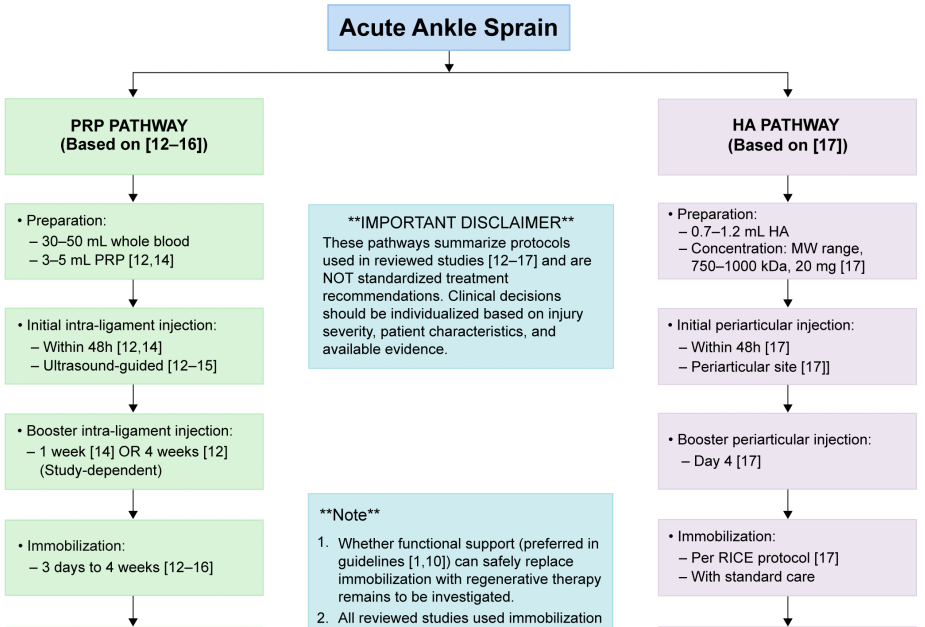
Guillo S, Bauer T, Lee JW, Takao M, Kong SW, Stone JW, et al. Consensus in chronic ankle instability: aetiology, assessment, surgical indications and place for arthroscopy. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 2013;99(8 Suppl):S411-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otsr.2013.10.009.
Doherty C, Bleakley C, Delahunt E, Holden S. Treatment and prevention of acute and recurrent ankle sprain: an overview of systematic reviews with meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med 2017;51(2):113-25. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2016-096178.
Halabchi F, Hassabi M. Acute ankle sprain in athletes: Clinical aspects and algorithmic approach. World J Orthop 2020;11(12):534-58. https://doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v11.i12.534.
Struijs PA, Kerkhoffs GM. Ankle sprain: the effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. BMJ Clin Evid 2015;2015:1115. PMID: 26218749.
Kemler E, van de Port I, Backx F, van Dijk CN. A systematic review on the treatment of acute ankle sprain: brace versus other functional treatment types. Sports Med 2011;41(3):185-97. https://doi.org/10.2165/11584370-000000000-00000.
Gaddi D, Mosca A, Piatti M, Munegato D, Catalano M, Di Lorenzo G, et al. Acute Ankle Sprain Management: An Umbrella Review of Systematic Reviews. Front Med (Lausanne) 2022;9:868474. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2022.868474.
Banerjee S, Mishra S, Rajnish RK, Yadav SK, Gupta S, Elhence A. Efficacy of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma for the Treatment of Ankle Sprain: A Systematic Review of Literature with Limited Meta-Analysis. Indian J Orthop 2025;59(7):910-9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43465-025-01418-1.
Zhang J, Wang C, Li X, Fu S, Gu W, Shi Z. Platelet-rich plasma, a biomaterial, for the treatment of anterior talofibular ligament in lateral ankle sprain. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2022;10:1073063. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2022.1073063.
Blanco-Rivera J, Elizondo-Rodríguez J, Simental-Mendía M, Vilchez-Cavazos F, Peña-Martínez VM, Acosta-Olivo C. Treatment of lateral ankle sprain with platelet-rich plasma: A randomized clinical study. Foot Ankle Surg 2020;26(7):750-4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fas.2019.09.004.
Laver L, Carmont MR, McConkey MO, Palmanovich E, Yaacobi E, Mann G, et al. Plasma rich in growth factors (PRGF) as a treatment for high ankle sprain in elite athletes: a randomized control trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2015;23(11):3383-92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-014-3119-x.
Lai MWW, Sit RWS. Healing of Complete Tear of the Anterior Talofibular Ligament and Early Ankle Stabilization after Autologous Platelet Rich Plasma: a Case Report and Literature Review. Arch Bone Jt Surg 2018;6(2):146-9. PMID: 29600268.
Rowden A, Dominici P, D'Orazio J, Manur R, Deitch K, Simpson S, et al. Double-blind, Randomized, Placebo-controlled Study Evaluating the Use of Platelet-rich Plasma Therapy (PRP) for Acute Ankle Sprains in the Emergency Department. J Emerg Med 2015;49(4):546-51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jemermed.2015.03.021.
Petrella MJ, Cogliano A, Petrella RJ. Original research: long-term efficacy and safety of periarticular hyaluronic acid in acute ankle sprain. Phys Sportsmed 2009;37(1):64-70. https://doi.org/10.3810/psm.2009.04.1684.
Chinn L, Hertel J. Rehabilitation of ankle and foot injuries in athletes. Clin Sports Med 2010;29(1):157-67, table of contents. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csm.2009.09.006.
Levine OP, Kondapi K, Tjong VK, Gohal C. Postinjection protocols following platelet-rich plasma administration for knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review. PM R 2024;16(9):1023-9. https://doi.org/10.1002/pmrj.13139.
Zhang Z, Liu P, Xue X, Zhang Z, Wang L, Jiang Y, et al. The role of platelet-rich plasma in biomedicine: A comprehensive overview. iScience 2025;28(2):111705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2024.111705.
Everts P, Onishi K, Jayaram P, Lana JF, Mautner K. Platelet-Rich Plasma: New Performance Understandings and Therapeutic Considerations in 2020. Int J Mol Sci 2020;21(20):7794. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207794.
Everts PA, Knape JT, Weibrich G, Schönberger JP, Hoffmann J, Overdevest EP, et al. Platelet-rich plasma and platelet gel: a review. J Extra Corpor Technol 2006;38(2):174-87. https://doi.org/10.1051/ject/200638174.
Elksniņš-Finogejevs A, Vidal L, Peredistijs A. Intra-articular platelet-rich plasma vs corticosteroids in the treatment of moderate knee osteoarthritis: a single-center prospective randomized controlled study with a 1-year follow up. J Orthop Surg Res 2020;15(1):257. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-020-01753-z.
Huang LH, Rau CS, Zeng WH, Lu TH, Wu YC, Chiu YH, et al. A new technique for separating platelet-rich plasma by a copolymer device - without a centrifugation process. Biomed Pharmacother 2022;153:113481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113481.
Frey C, Yeh PC, Jayaram P. Effects of Antiplatelet and Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Medications on Platelet-Rich Plasma: A Systematic Review. Orthop J Sports Med 2020;8(4):2325967120912841. https://doi.org/10.1177/2325967120912841.
Atchison JW, Herndon CM, Rusie E. NSAIDs for musculoskeletal pain management: current perspectives and novel strategies to improve safety. J Manag Care Pharm 2013;19(9 Suppl A):S3-19. https://doi.org/10.18553/jmcp.2013.19.s9.1.
Wang B, Wu L, Chen J, Dong L, Chen C, Wen Z, et al. Metabolism pathways of arachidonic acids: mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2021;6(1):94. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-020-00443-w.
Yan M, Wang Z, Qiu Z, Cui Y, Xiang Q. Platelet signaling in immune landscape: comprehensive mechanism and clinical therapy. Biomark Res 2024;12(1):164. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40364-024-00700-y.
Tarnawski AS, Jones MK. Inhibition of angiogenesis by NSAIDs: molecular mechanisms and clinical implications. J Mol Med (Berl) 2003;81(10):627-36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-003-0479-y.
Qiao X, Yan L, Feng Y, Li X, Zhang K, Lv Z, et al. Efficacy and safety of corticosteroids, hyaluronic acid, and PRP and combination therapy for knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2023;24(1):926. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-023-06925-6.
Karasavvidis T, Totlis T, Gilat R, Cole BJ. Platelet-Rich Plasma Combined With Hyaluronic Acid Improves Pain and Function Compared With Hyaluronic Acid Alone in Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Arthroscopy 2021;37(4):1277-87.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arthro.2020.11.052.
Zhao J, Huang H, Liang G, Zeng LF, Yang W, Liu J. Effects and safety of the combination of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and hyaluronic acid (HA) in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2020;21(1):224. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-020-03262-w.
Papalia R, Zampogna B, Russo F, Torre G, De Salvatore S, Nobile C, et al. The combined use of platelet rich plasma and hyaluronic acid: prospective results for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 2019;33(2 Suppl. 1):21-8. PMID: 31168999.
Filardo G, Previtali D, Napoli F, Candrian C, Zaffagnini S, Grassi A. PRP Injections for the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Cartilage 2021;13(1_suppl):364S-75S. https://doi.org/10.1177/1947603520931170.
Fossati C, Randelli FMN, Sciancalepore F, Maglione D, Pasqualotto S, Ambrogi F, et al. Efficacy of intra-articular injection of combined platelet-rich-plasma (PRP) and hyaluronic acid (HA) in knee degenerative joint disease: a prospective, randomized, double-blind clinical trial. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2024;144(11):5039-51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-024-05603-z.
DeLong JM, Russell RP, Mazzocca AD. Platelet-rich plasma: the PAW classification system. Arthroscopy 2012;28(7):998-1009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arthro.2012.04.148.
Magalon J, Chateau AL, Bertrand B, Louis ML, Silvestre A, Giraudo L, et al. DEPA classification: a proposal for standardising PRP use and a retrospective application of available devices. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med 2016;2(1):e000060. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjsem-2015-000060.
Mishra A, Harmon K, Woodall J, Vieira A. Sports medicine applications of platelet rich plasma. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 2012;13(7):1185-95. https://doi.org/10.2174/138920112800624283.
Medina-Porqueres I, Martin-Garcia P, Sanz-De-Diego S, Reyes-Eldblom M, Moya-Torrecilla F, Mondragon-Cortes R, et al. Platelet-Rich Plasma Injections in Chronic Lateral Ankle Instability: A Case Series. Biomedicines 2024;12(5):963. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12050963.
Sabaghzadeh A, Zarei Kurdkandi H, Ebrahimpour A, Biglari F, Jafari Kafiabadi M. Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma for Chronic Lateral Ankle Instability After Modified Broström-Gould surgery: A Randomized, Single-Blinded, Prospective Controlled Trial. Foot Ankle Orthop 2023;8(2):24730114231168633. https://doi.org/10.1177/24730114231168633.
Urits I, Hasegawa M, Orhurhu V, Peck J, Kelly AC, Kaye RJ, et al. Minimally Invasive Treatment of Chronic Ankle Instability: a Comprehensive Review. Curr Pain Headache Rep 2020;24(3):8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11916-020-0840-7
Downloads
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Yu-Tung Chen, Wen-Tien Wu, Ru-Ping Lee, Tzai-Chiu Yu, Ing-Ho Chen, Kuang-Ting Yeh

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









