Preprocedural systemic immune-inflammation index predicts atrial fibrillation recurrence after catheter ablation: A systematic review and meta-analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2026.13614Keywords:
Systemic immune-inflammation index, atrial fibrillation, catheter ablation, recurrence, meta-analysisAbstract
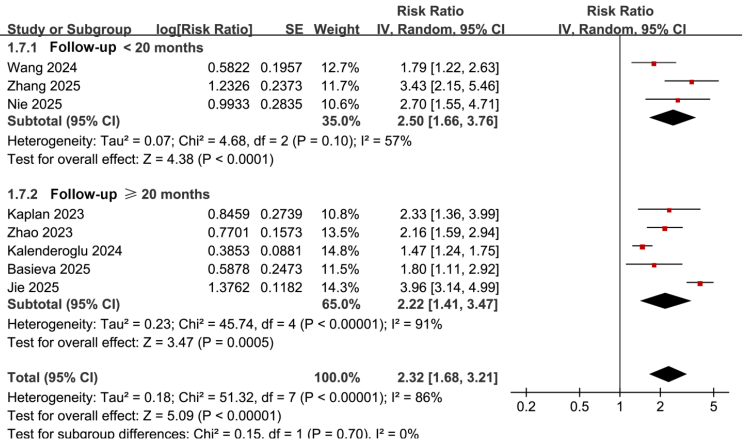
Inflammation plays a significant role in the pathophysiology of atrial fibrillation (AF) and may affect the likelihood of AF recurrence following catheter ablation. The systemic immune-inflammation index (SII), calculated from circulating neutrophils, lymphocytes, and platelets, has emerged as a promising inflammatory biomarker. This meta-analysis aimed to assess the relationship between preprocedural SII and the recurrence of AF post-ablation. We conducted comprehensive searches across PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, Wanfang, and China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) for longitudinal observational studies reporting the correlation between preprocedural SII and AF recurrence after either radiofrequency or cryoballoon ablation. Risk ratios (RRs) were aggregated using random-effects models to account for heterogeneity. A total of ten cohort studies involving 4,045 patients were included in the analysis. Our findings indicate that a high preprocedural SII is significantly associated with an increased risk of AF recurrence (RR = 2.32, 95% CI 1.68–3.21; I² = 86%). This association remained robust across sensitivity analyses (RR range 2.07–2.53) and showed consistency across predefined subgroups based on sample size (<400 vs. ≥400), age (<61 vs. ≥61 years), sex distribution (<60% vs. ≥60% men), SII cutoff (<510 vs. ≥510), ablation modality (RFCA vs. CBA), follow-up duration (<20 vs. ≥20 months), and study quality (all p for subgroup differences >0.05), although these subgroup analyses were exploratory in nature. Meta-regression did not reveal significant study-level modifiers. Additionally, a further meta-analysis treating SII as a continuous variable demonstrated that each 100-unit increase in SII correlates with a higher recurrence risk (RR = 1.09, 95% CI 1.04–1.13; I² = 43%). In conclusion, elevated preprocedural SII is associated with an increased risk of AF recurrence after catheter ablation, indicating that SII may serve as a potential adjunctive marker of inflammatory status, pending further prospective validation.
Citations
Downloads
References
Martin SS, Aday AW, Allen NB, Almarzooq ZI, Anderson CAM, Arora P, et al. 2025 heart disease and stroke statistics: a report of US and global data from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2025;151(8):e41–e660.
Bizhanov KA, Abzaliyev KB, Baimbetov AK, Sarsenbayeva AB, Lyan E. Atrial fibrillation: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and clinical complications (literature review). J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2023;34(1):153–65.
https://doi.org/10.1111/jce.15759
Linz D, Gawalko M, Betz K, Hendriks JM, Lip GYH, Vinter N, et al. Atrial fibrillation: epidemiology, screening and digital health. Lancet Reg Health Eur. 2024;37:100786.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lanepe.2023.100786
Hussain S, Sohrabi C, Providencia R, Ahsan S, Papageorgiou N. Catheter ablation for the management of atrial fibrillation: an update of the literature. Life (Basel). 2023;13(8):1784.
https://doi.org/10.3390/life13081784
Andrade JG. Ablation as first-line therapy for atrial fibrillation. Eur Cardiol. 2023;18:e46.
https://doi.org/10.15420/ecr.2023.04
Darby AE. Recurrent atrial fibrillation after catheter ablation: considerations for repeat ablation and strategies to optimize success. J Atr Fibrillation. 2016;9(1):1427.
Li S, Zhang J, Zuo S, Wang J, Lai Y, Li M, et al. Patterns of postablation recurrence and adverse cardiovascular outcomes in patients with atrial fibrillation. J Am Heart Assoc. 2025;14(9):e038832.
https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.124.038832
Mo D, Wang M, Zhang P, Dai H, Guan J. Factors predicting the recurrence of atrial fibrillation after catheter ablation: a review. Heliyon. 2024;10(13):e34205.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34205
Nso N, Bookani KR, Metzl M, Radparvar F. Role of inflammation in atrial fibrillation: a comprehensive review of current knowledge. J Arrhythm. 2021;37(1):1–10.
https://doi.org/10.1002/joa3.12473
Zhou X, Dudley SC Jr. Evidence for inflammation as a driver of atrial fibrillation. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2020;7:62.
https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2020.00062
Ye Z, Hu T, Wang J, Xiao R, Liao X, Liu M, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index as a potential biomarker of cardiovascular diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022;9:933913.
https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2022.933913
Zhao Z, Zhang X, Sun T, Huang X, Ma M, Yang S, et al. Prognostic value of systemic immune-inflammation index in CAD patients: systematic review and meta-analyses. Eur J Clin Invest. 2024;54(2):e14100.
https://doi.org/10.1111/eci.14100
Chen YC, Liu CC, Hsu HC, Hung KC, Chang YJ, Ho CN, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index for predicting postoperative atrial fibrillation following cardiac surgery: a meta-analysis. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024;11:1290610.
https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2024.1290610
Korantzopoulos P, Letsas KP, Tse G, Fragakis N, Goudis CA, Liu T. Inflammation and atrial fibrillation: a comprehensive review. J Arrhythm. 2018;34(4):394–401.
https://doi.org/10.1002/joa3.12077
Kaplan E, Ekizler FA, Saribaş H, Tak BT, Cay S, Korkmaz A, et al. Effectiveness of the systemic immune inflammation index to predict atrial fibrillation recurrence after cryoablation. Biomark Med. 2023;17(2):101–9.
https://doi.org/10.2217/bmm-2022-0515
Zhao Z, Jiang B, Zhang F, Ma R, Han X, Li C, et al. Association between the systemic immune-inflammation index and outcomes among atrial fibrillation patients with diabetes undergoing radiofrequency catheter ablation. Clin Cardiol. 2023;46(11):1426–33.
https://doi.org/10.1002/clc.24116
Gu P, Xu P, Chen Y, Li J, Sun H, Xu H, et al. The predictive value of pan-immune inflammatory index for early recurrence of atrial fibrillation after cryoablation. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024;24(1):669.
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-024-04329-5
Kalenderoglu K, Hayiroglu MI, Cinar T, Oz M, Bayraktar GA, Cam R, et al. Comparison of inflammatory markers for the prediction of atrial fibrillation recurrence following cryoablation. Biomark Med. 2024;18(17–18):717–25.
https://doi.org/10.1080/17520363.2024.2395236
Wang YJ, Liu KS, Meng XJ, Han XF, Nie LJ, Feng WJ, et al. Role of a new inflammation predictor in predicting recurrence of atrial fibrillation after radiofrequency catheter ablation. World J Cardiol. 2024;16(12):740–50.
https://doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v16.i12.740
Basieva MA, Shvarts VA, Sokolskaya MA, Donakanyan SA, Filatov AG, Avanesyan GA, et al. Role of novel indices of systemic inflammation in atrial fibrillation recurrence after cryoballoon pulmonary vein isolation. Cardiovasc Ther Prev. 2025;24(7):14–23.
https://doi.org/10.15829/1728-8800-2025-4417
Guo YT, Zhang JD. Study on the correlation between systemic immunoinflammatory index and recurrence of atrial fibrillation after radiofrequency ablation. Adv Clin Med. 2025;15(7):123–31.
https://doi.org/10.12677/acm.2025.1571966
Jie Q, Qian W, Jia H, Zhang F, Wang J. Prognostic value of inflammatory indices for atrial fibrillation recurrence after cryoablation: a cohort study. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025;12:1637255.
https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2025.1637255
Nie L, Nie Q, Liu K, Zhang S, Wang Y, Yu Y, et al. The predictive value of the neutrophil percentage-to-albumin ratio for early recurrence of atrial fibrillation after radiofrequency catheter ablation. J Inflamm Res. 2025;18:15615–26.
https://doi.org/10.2147/JIR.S557322
Zhang Z, Li S, Tu T, Liu C, Dai Y, Wang C, et al. Nonlinear relationship and predictive value of systemic immune-inflammation index for atrial fibrillation recurrence after catheter ablation in hypertensive patients. Heart Rhythm. 2025;22(9):2257–68.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2025.03.1958
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;372:n71.
https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n71
Higgins J, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page M, et al. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 6.2. The Cochrane Collaboration. 2021.
www.training.cochrane.org/handbook
Wells GA, Shea B, O'Connell D, Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M, et al. The Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. 2010.
http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp
Zhang J, Yu KF. What’s the relative risk? A method of correcting the odds ratio in cohort studies of common outcomes. JAMA. 1998;280(19):1690–1.
https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.280.19.1690
Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 2002;21(11):1539–58.
https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.1186
Marušić MF, Fidahić M, Cepeha CM, Farcaș LG, Tseke A, Puljak L. Methodological tools and sensitivity analysis for assessing quality or risk of bias used in systematic reviews published in the high-impact anesthesiology journals. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2020;20(1):121.
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-020-00966-4
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997;315(7109):629–34.
https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629
Hu J, Huang L, Zhao X, Jin N, Hong J, Rong J. Strong positive correlations between the levels of systemic inflammation markers and the occurrence of persistent atrial fibrillation. Int Heart J. 2024;65(6):1004–11.
https://doi.org/10.1536/ihj.23-665
Zhao X, Huang L, Hu J, Jin N, Hong J, Chen X. The association between systemic inflammation markers and paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024;24(1):334.
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-024-04004-9
Morrissey SM, Kirkland LG, Phillips TK, Levit RD, Hopke A, Jensen BC. Multifaceted roles of neutrophils in cardiac disease. J Leukoc Biol. 2025;117(4).
https://doi.org/10.1093/jleuko/qiaf017
Gros A, Ollivier V, Ho-Tin-Noé B. Platelets in inflammation: regulation of leukocyte activities and vascular repair. Front Immunol. 2014;5:678.
https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2014.00678
Wang X, Chen L, Wei J, Zheng H, Zhou N, Xu X, et al. The immune system in cardiovascular diseases: from basic mechanisms to therapeutic implications. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025;10(1):166.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-025-02220-z
Chi R, Shan X, Guan C, Yang H, Wang X, Li B, et al. Association between systemic inflammatory response index and left ventricular remodeling and systolic dysfunction in atrial fibrillation patients. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023;23(1):377.
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-023-03403-8
Vlachakis PK, Theofilis P, Apostolos A, Karakasis P, Ktenopoulos N, Boulmpou A, et al. Beyond pulmonary vein reconnection: exploring the dynamic pathophysiology of atrial fibrillation recurrence after catheter ablation. J Clin Med. 2025;14(9):2919.
https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14092919
Kim S. Overview of clinical study designs. Clin Exp Emerg Med. 2024;11(1):33–42.
https://doi.org/10.15441/ceem.23.036
Dolu AK, Akçay FA, Atalay M, Karaca M. Systemic immune-inflammation index as a predictor of left atrial thrombosis in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. J Tehran Heart Cent. 2023;18(2):87–93.
https://doi.org/10.18502/jthc.v18i2.13317
Kuş G, Çağırcı G, Bayar N, Özgünoğlu EC, Güven R, Arslan Ş. Usefulness of the systemic immune-inflammation index in predicting atrial fibrillation recurrence after direct current cardioversion. Biomark Med. 2022;16(11):847–55.
https://doi.org/10.2217/bmm-2022-0120
Luo Y, Zhang J, Liu T, Yin Z, Jin Y, Han J, et al. The systemic-immune-inflammation index predicts the recurrence of atrial fibrillation after cryomaze concomitant with mitral valve surgery. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2022;22(1):45.
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-022-02494-z
Yakut I, Konte HC, Ozeke O. Exploring inflammatory markers and risk factors associated with pericarditis development after ablation for atrial fibrillation. J Clin Med. 2024;13(19):5934.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2026 Bingshan Zhang, Shourong Lu, Zhehao Yin, Kaicheng Wang

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









