Expression of phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase in rat kidneys exposed to high +Gz
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2012.2453Keywords:
Gz acceleration, rat, kidney, extracellular signal-regulated kinase, immunohistochemistryAbstract
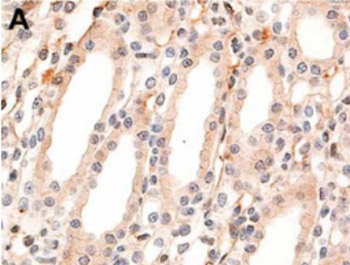
Exposure to high gravitational acceleration forces acting along the body axis from the head to the feet (+Gz) severely reduces blood flow to the visceral organs, including the kidneys. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) figures predominantly in mediating kidney cell responses to a wide variety of stress-related stimuli. Though previous studies have shown the activation of ERK in some experimental models, the regulation of ERK associated with +Gz exposure has not yet been investigated. The aim of this study was to examine the effect of high +Gz exposure on ERK activation in the kidneys. Using a small animal centrifuge, eight male Sprague-Dawley rats were exposed to +10Gz or +13Gz three times for 3 minutes each. The bilateral kidneys were obtained from each rat, and the expression levels of phosphorylated ERK (p-ERK) were evaluated using immunohistochemistry. In the control group, the collecting duct epithelium displayed faint cytoplasmic staining with no nuclear staining of p-ERK. By contrast, rats exposed to +10Gz showed strong nuclear staining intensity for p-ERK. In the renal papilla, the epithelial cells of collecting ducts and thin segments of the loop of Henle exhibited strong nuclear immunoreactivity for p-ERK. Rats exposed to +13Gz also showed the same staining intensity and distribution of p-ERK expression as that of rats exposed to +10Gz. This study is the first to describe +Gz exposure-induced alteration in the expression of p-ERK in the kidneys. Our finding suggests that high +Gz exposure leads to the activation of ERK in the renal papilla.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
Accepted 2017-09-14
Published 2012-11-20









