Comparative study of three rat models of stress urinary incontinence
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2011.2587Keywords:
stress urinary incontinence (SUI), animal model, rat, urodynamicsAbstract
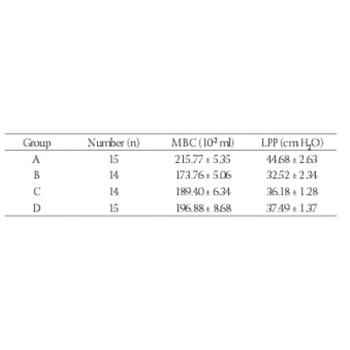
The aim of this study was to establish three rat models of stress urinary incontinence (SUI) and investigate the differences in urodynamics and success rate of establishing each model. Sixty healthy female SD rats were randomly divided into 4 groups of 15 rats each: A: control group; B: urethrolysis group; C: ovariectomy with colpectasis group; and D: colpectasis only group. Abdominal leak point pressure (LPP) and maximum bladder capacity (MBC) were calculated. The sneeze test was used to examine whether or not liquid leakage occurred at the urethral meatus in each model. LPP and MBC values were significantly lower in all experimental groups (groups B, C, and D) when compared to the control group A (p < 0.001). Within the experimental groups, the MBC and LPP of group B was the lowest, while these values in groups C and D were relatively higher (p < 0.001). However, there was no significant difference in LPP between groups C and D (p > 0.05). The positive rates of the sneeze test in groups A, B, C, and D were 0%, 86%, 64%, and 40%, respectively. We observed significant differences between the experimental groups and the control group (p < 0.05). Three methods (urethrolysis, colpectasis with an ovariectomy, and colpectasis only) can be successfully used to establish models of SUI in rats. Significant differences in urodynamics and the successful establishment of the model occurred in this study.
Citations
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
How to Cite
Accepted 2017-10-20
Published 2011-05-20









