Echocardiographic Evaluation of Cardiac Function in Female Patients with Thyroid Disorders
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2010.2704Keywords:
hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, cardiac function, echocardiographyAbstract
The aim of this study was to assess echocardiographic changes in female patients with untreated dysfunctional thyroid states and whether the therapy aimed to normalize the thyroid dysfunction could lead to improvement in cardiac systolic and diastolic function. The study included 90 female subjects who performed control of thyroid hormonal status at the Institute of Nuclear Medicine at the University of Sarajevo Clinics Centre and who previously were untreated for the thyroid functional disorders. The study sample was divided in three groups based on the thyroid hormones levels: a) hyperthyroid group (n= 30) b) hypothyroid group (n=30) and c) euthyroid (control). Echocardiography measurements were performed on commercially available Toshiba, SSH 140.
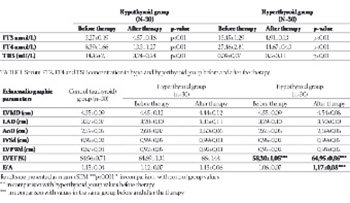
Before the therapy no statistically significant differences in the peak early and late mitral inflow velocities (E/A) values between the study groups was observed, but the mean left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) in hypothyroid group was significantly lower (58,30±1,05) compared to control (64,96±0,71) and hyperthyroid group (64,69±1,31) (p<0,001). In hypothyroid group we found significant increase in mean LVEF (58,30±1,05 vs. 64,95±0,86, p<0,01) and E/A (1,06±0,07 vs. 1,17±0,08; p=0,01) values after the normalization of thyroid hormone status. Thyroid dysfunctional states were not associated with impaired diastolic function, probably due to the short duration of thyroid dysfunction and timely and successful conversion therapy. Systolic function however was significantly reduced in hypothyroid patients but subsequently improved after the adequate therapy. Early diagnostic approach in patients with thyroid dysfunctional states is important for avoidance of cardiac complications that accompany these disorders.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
How to Cite
Accepted 2017-11-23
Published 2010-05-20









