Significantly Reduced Salivary Nitric Oxide Synthesis in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2005.3277Keywords:
nitric oxide, Parkinson’s disease, salivaAbstract
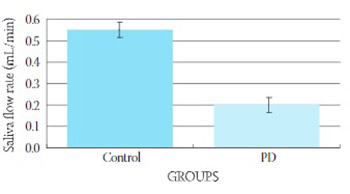
In order to study concentration of nitric oxide (NO) in the saliva of patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD), we measured the concentration of its stable metabolite nitrite (NO2-) in the saliva of these patients and healthy subjects. We analyzed saliva flow rate and salivary NO concentrations in 16 subjects with Parkinson’s disease and in 16 healthy subjects. Concentration of nitrite was determined by colorimetric method using Griess reaction. Saliva flow rate was significantly lower in patients with Parkinson’s disease (0,2±0,03 mL/min; X±SEM) than in healthy subjects. Salivary NO2-concen-tration was significantly lower (5,0210,64) than in healthy individuals (22,3911,24; p<0,0001).
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
How to Cite
Accepted 2018-03-02
Published 2005-08-20









