Changes in blood vessels in fetuses 4 to 9 months intrauterine life old by postmortem angiography method
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2004.3394Keywords:
brain, fetuses, cerebral blood vesselsAbstract
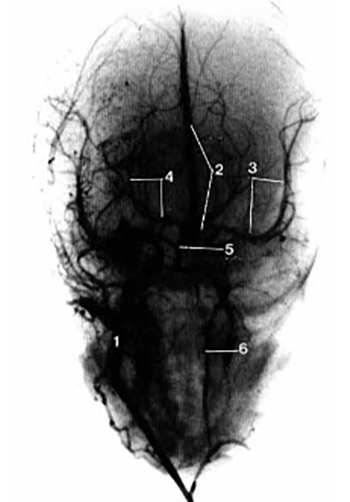
We monitored changes in caliber, position and branching of blood vessels in fetuses of 4 - 9 months of intrauterine life. By precise dissection we prepared starting parts of common carotid artery and internal jugular vein in 40 cadaver fetuses. The vessels were injected with Telebrix and subjected to postmortem angiography at the Institute of Radiology Clinics Center in Sarajevo. Thereafter, arteries obtained were compared and analyzed. In preparations of few months old fetal material we observed arteries of fairly straight course, low caliber and with no observable ramification. When preparations of more mature stillborn infants were examined, we detected arteries of undulating course, more expressed ramification and higher caliber. In stillborn babies, all three arteries are of high caliber with rich branching. Considering that in this phase of brain development sulcuses are relatively wide, we can say that course of arteries is partially tortuous. Analysis of venous vessels shows good distinction of venous sinuses and sub-arachnoidal cisterns. We can conclude with great certainty that the changes occur in position, caliber and relationship among vessels in fetus during the period of brain sulci and gyri formation.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Accepted 2018-03-20
Published 2004-08-20









