Protective effect of neonatal BCG vaccines against tuberculous meningitis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2004.3460Keywords:
BCG neonatal vaccine, protective efficacy, newbornsAbstract
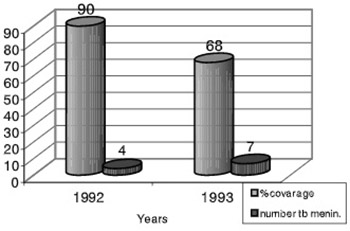
Neonatal BCG vaccination reduces the risk of tuberculosis and provides protection higher than 80% against the development of meningeal and miliary tuberculosis in newborns. Tuberculosis meningitis remains a major problem and also an important cause of death in some countries. In countries with high and moderate incidence of tuberculosis, prevention from the most severe complications of tuberculosis can be achieved only with a high coverage of the universal BCG neonatal immunization, being higher than 98% in the cohort of newborns. The decrease in BCG immunization coverage within immunization program during the year 2003 in Bosnia and Herzegovina influenced the increase in tuberculous meningitis. During 2002, when coverage with BCG vaccination in cohort of newborns was 90%, the incidence rate of tuberculous meningitis was 19. 04 ‰ . With the 68% decrease in BCG immunization coverage in the cohort of newborns in Bosnia and Herzegovina during the year 2003, the incidence of tuberculous meningitis raised to 33 33 ‰ . It has been proven that the 22% decrease of the neonatal BCGimmunization coverage in the cohort of newborns /vaccination program of children/ caused 175 times higher number of the tuberculous meningitis cases. Newborns affected by the tuberculous meningitis were not BCG vaccinated. BCG vaccineprovided effective protection against tuberculous meningitis, as well against the death of newborns caused by tuberculosis.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
How to Cite
Accepted 2018-04-05
Published 2004-02-20









