The effects of McKenzie exercises for patients with low back pain, our experience
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2003.3497Keywords:
McKenzie exercises, Low Back Pain, Pain measurements, CentralisationAbstract
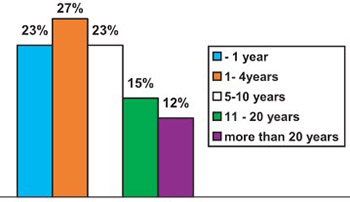
To investigate the influence of McKenzie exercises on decreasing the pain in patients with low back pain, to show the occurrence of Centralization sign, as a predictor of good treatment outcomes and to evaluate the use of McKenzie exercises, as a routine method for lower back pain in Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Centres. We conducted a clinical, prospective, manipulative study in Physiotherapy and Rehabilitation Clinic in Community Based Rehabilitation Centers and Institute for Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation affiliated with a Medical College Sarajevo. We included 34 patients with symptoms of low back pain. The patients were subjected to McKenzie exercise program for low back pain performed individually to the need and possibility of each patient. Patients attended exercise programs daily, under the supervision of physiatrist and physiotherapist and do it also at home, five times a day in series of 5 to 10 repetitions each time, depending on the stage of disease and pain intensity. The average training period was 15.5 days. All patients were assessed before and after the treatment. Visual Analog Scale (VAS) measured intensity of pain, localization of pain was noted on special forms and the Shober test was used to show differences in spinal movement before and after the treatment. Measurements of spinal movements and flexibility of the spine showed significant improvement in all patients. The average difference in values of the Shober test before and after treatment was 1.1 cm with SD 0.98. The difference test was t=6.263 with a significant difference of p<0.01. Mean pain intensity was reduced significantly as a result of treatment. The pain was reduced on VAS for X=2,8 with S.D. 1.56. The difference Test was t=10.332, with significant difference p<0.01. 61.5% of the total number of participants had signs of centralization (6% were in the acute stage of pain, 32% in subacute and 23,5% in chronic pain). Centralization sign was noted in 40% of acute patients, 57.5% subacute and 80% of chronic patients with a low back pain who exercised McKenzieprogram. McKenzie exercises for low back pain are a beneficial treatment for increasing flexibility of the spine and improving the pain with better results in pain relief. Although done by minimally trained physiotherapists in the McKenzie approach, McKenzie exercises are a successful method for decreasing and centralizing the pain and increasing spinal movements in patients with low back pain.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
How to Cite
Accepted 2018-04-14
Published 2003-11-20









