Erythrocyte D -Aminolevulinic Acid Dehydratase (Ala-D) Activity and Blood Lead Level (Pb-B) of Tortoise (Testudo Hemanni, Gmel.) of Vicinity of Lead and Zinc Smelter “Trepca” in Kosova
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.1998.3609Keywords:
ERYTHROCYTE, d - AMINOLEWLINIC ACID DEHYDRATASE, TORTOISEAbstract
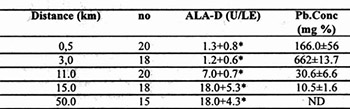
In comparison with control animals, a significant negative correlation (r = 0.77 -), between lead level and the activity of daminolevulinic acid dehydratase activity in the blood of land turtle (Testudo hermanni, Gmel.) caught in five different localities from heavy polluted environment of lead and zinc smelter “Trepca” was found. The concentration ratio of lead level in blood between control animals and those from the vicinity of smelter was 10:160 % and ratio of ALA-D activity was 10:18,3 U/LE.
Citations
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Accepted 2018-05-14
Published 1998-01-20









