Decreased heart rate recovery may predict a high SYNTAX score in patients with stable coronary artery disease
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2019.3725Keywords:
Heart rate recovery, SYNTAX score, coronary artery disease, CAD, HRRAbstract
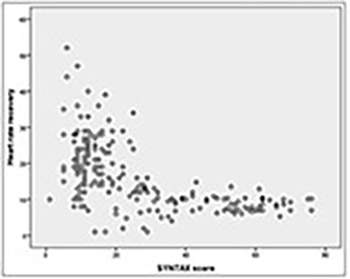
An impaired heart rate recovery (HRR) has been associated with increased risk of cardiovascular events, cardiovascular, and all‐cause mortality. However, the diagnostic ability of HRR for the presence and severity of coronary artery disease (CAD) has not been clearly elucidated. Our aim was to investigate the relationship between HRR and the SYNTAX (SYNergy between percutaneous coronary intervention with TAXus and cardiac surgery) score in patients with stable CAD (SCAD). A total of 406 patients with an abnormal treadmill exercise test and ≥50% coronary stenosis on coronary angiography were included. The HRR was calculated by subtracting the HR in the first minute of the recovery period from the maximum HR during exercise. The SYNTAX score ≥23 was accepted as high. Correlation of HRR with SYNTAX score and independent predictors of high SYNTAX score were determined. A high SYNTAX score was present in 172 (42%) patients. Mean HRR was lower in patients with a high SYNTAX score (9.8 ± 4.5 vs. 21.3 ± 9, p < 0.001). The SYNTAX score was negatively correlated with HRR (r: -0.580, p < 0.001). In multivariate logistic regression analysis, peripheral arterial disease (OR: 13.3; 95% CI: 3.120–34.520; p < 0.001), decreased HRR (OR: 0.780; 95% CI: 0.674–0.902; p = 0.001), peak systolic blood pressure (OR: 1.054; 95% CI: 1.023–1.087; p = 0.001), and peak HR (OR: 0.950; 95% CI: 0.923–0.977; p < 0.001) were found to be independent predictors of a high SYNTAX score. Our results showed that HRR is significantly correlated with the SYNTAX score, and a decreased HRR is an independent predictor of a high SYNTAX score in patients with SCAD.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
How to Cite
Accepted 2018-08-12
Published 2019-02-12









