Association of serum chemerin and inflammatory factors with type 2 diabetes macroangiopathy and waist-to-stature ratio
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2019.4002Keywords:
Type 2 diabetes, T2DM, macroangiopathy, chemerin, inflammatory factor, glycolipid metabolismAbstract
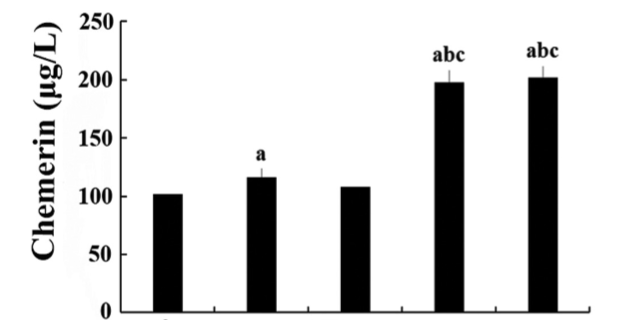
Chemerin is an adipocytokine that participates in glycolipid metabolism; however, its association with type 2 diabetes (T2DM) with lower extremity macroangiopathy (T2DM-V) has rarely been reported. This study explored the association of chemerin and inflammatory factors with body fat parameters, glucolipid metabolism, and insulin resistance (IR) in T2DM and T2DM-V. Patients were classified into normal glucose regulation (NGR), T2DM, and T2DM-V groups. Serum chemerin, glucolipid metabolic parameters, transforming growth factor (TGF)-β, interleukin (IL)-6, monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-1, and fasting insulin levels were measured along with HOMA-IR, body mass index (BMI), and waist-to-stature ratio (WSR). Serum chemerin, TGF-β, IL-6, and MCP-1 levels were significantly higher in T2DM groups than in NGR group, and BMI, WSR, fasting plasma glucose (FPG), 2hPG, glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), triglycerides (TG), and HOMA-IR were higher in T2DM-V subgroups with moderate or severe lower extremity macroangiopathy than in NGR group, simple T2DM group, and T2DM-V subgroup with mild macroangiopathy. FPG, 2hPG, HbA1c, TG, and HOMA-IR were higher in T2DM-V subgroup with severe macroangiopathy than in T2DM-V with moderate macroangiopathy (p < 0.05). In all groups, serum chemerin levels were positively correlated with BMI, WSR, FPG, 2hPG, HbA1c, fasting insulin, aspartate transaminase, TG, TGF-β, IL-6, and HOMA-IR (p < 0.05) and negatively correlated with high-density lipoprotein cholesterol [HDL-c] (p < 0.05). Multiple stepwise regression analysis showed that 2hPG, HbA1c, and HDL-c were independent predictors of serum chemerin levels (β = -0.768, -0.122, -0.115, and 3.261, respectively; p < 0.01). Collectively, chemerin, factors associated with obesity, pathological and physiological changes in glucolipid metabolism, and inflammatory factors may promote the development of T2DM macroangiopathy.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2019 Association of Basic Medical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2019-04-11
Published 2019-11-08









