Expression patterns and prognostic value of miR-210, miR-494, and miR-205 in middle-aged and old patients with sepsis-induced acute kidney injury
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2019.4131Keywords:
microRNA, Sepsis, Acute kidney injury, Prognosis, Predictive valueAbstract
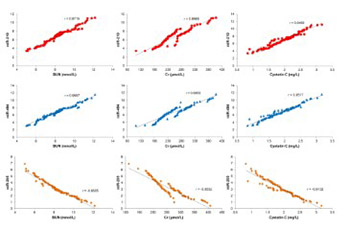
Septic patients suffer a ‘cytokine storm’ from proinflammatory cytokines, chemokines and other inflammatory mediators, resulting in acute kidney injury (AKI) and death. The purpose of the present study was to determine the expression patterns of microRNA-210 (miR-210), miR-494, and miR-205 in middle-aged and old patients with sepsis-induced AKI and to evaluate their association with patient prognosis. Serum blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine (Cr) and cystatin C levels were determined in peripheral venous blood collected from 110 patients with sepsis-induced AKI and 110 healthy controls. The expression profile of 30 miRNAs was analyzed by TaqMan low-density array (TLDA) in plasma samples from patients and controls. Association of miRNAs with prognosis and survival of patients was analyzed by Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient, Cox multivariate analysis, and ROC curve analysis. TILDA analysis showed 11 upregulated and 11 downregulated miRNAs in patients with sepsis-induced AKI. MiR-210 and miR-494 were the most upregulated and miR-205 was the most downregulated miRNA. High expression of miR-210 and miR-494 was positively correlated with BUN, Cr and cystatin C levels of patients, while low expression of miR-205 was negatively correlated. MiR-210 and miR-494 expression was significantly decreased and miR-205 expression was increased in survivors with sepsis-induced AKI (28-day survival, n = 68) vs. non-survivors (n = 42). BUN, Cr, and miR-205 were independent risk factors for prognosis in sepsis-induced AKI. Our study showed the predictive value of miR-210, miR-494, and miR-205 in prognosis and survival of patients with sepsis-induced AKI. MiR-205 is an independent risk factor for sepsis-induced AKI and its decreased expression is associated with shorter patient survival.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
Accepted 2019-02-27
Published 2019-08-20









