Concordance of PD-L1 expression and CD8+ TIL intensity between NSCLC and synchronous brain metastases
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2019.4474Keywords:
Programmed death-ligand 1, non-small-cell lung cancer, NSCLC, tumor immunology, PD-L1, brain metastasis, CD8 lymphocytes, tumor infiltrating lymphocytes, TILsAbstract
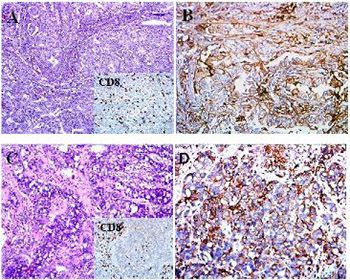
Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) is suggested to be a predictive biomarker in non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC). However, the differential expression of PD-L1 in primary lung tumor vs. synchronous metastases, especially brain metastasis (BM), remains unclear. This study assessed the concordance of PD-L1 expression on tumor cells and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) and CD8+ TIL intensity between primary lung tumors and synchronous BMs from 24 NSCLC patients. PD-L1, CD3, and CD8 positivity was determined by immunohistochemistry (IHC). PD-L1 scoring was based on the proportion of tumor cells with membranous expression of PD-L1 and the cutoff values <1%, 1–49%, and ≥50%. CD3 and CD8 positivity in TILs was evaluated semi-quantitatively and the proportion of CD3+/CD8+ TILs was determined. PD-L1 expression on tumor cells and TILs was evaluated in relation to CD3+/CD8+ TIL proportions and the intensity of CD8+ TILs between the paired primary lung and BM tissues. In the primary lung tumors, PD-L1 positivity was observed in 25%, 37.5%, and 37.5% cases for the cutoff values <1%, 1–49%, and ≥50%, respectively. PD-L1 expression on tumor cells was strongly correlated between the paired primary lung and BM tissues, in all cutoff groups. However, PD-L1 expression on TILs and the proportion of CD3+/CD8+ TILs were not strongly correlated in all three groups between the paired primary lung tumors and BMs. The intensity of CD8+ TILs was concordant in only 54.16% of the paired primary lung tumors and BMs. This study showed a high concordance of PD-L1 expression in neoplastic cells between primary NSCLC and synchronous BMs.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
How to Cite
Accepted 2019-11-13
Published 2020-08-03









