Overexpression of microRNA-129-5p in glioblastoma inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and colony-forming ability by targeting ZFP36L1
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2019.4503Keywords:
Glioblastoma multiforme, GBM, microRNA, miR-129-5p, ZFP36L1, migration, proliferation, colony-forming ability, tumor-suppressorAbstract
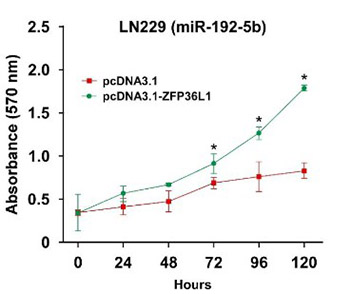
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is a highly invasive cancer with a high recurrence rate. The prognosis of GBM patients remains poor, even after standard surgical resection combined with chemoradiotherapy. Thus, there is an urgent need for new therapeutic targets in GBM. In recent years, microRNAs have received considerable attention due to their important role in tumor development and progression. In this study, we investigated the role of miR-129-5p and miR-129-5p/ZFP36L1 axis in GBM tumorigenesis. Analysis of GSE103228 microarray data from the GEO database showed that miR-129-5p was significantly downregulated in GBM vs. normal brain tissues. Quantitative reverse transcription PCR analysis of miR-129-5p expression in seven GBM cell lines (LN229, A172, U87, T98G, U251, H4, and LN118) vs. normal human astrocytes (NHA) showed miR-129-5p was significantly downregulated in GBM cells. Overexpression of miR-129-5p in LN229 and A172 cells significantly suppressed cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and colony-forming ability. Target Scan analysis identified ZFP36L1 as the target of miR-129-5p. UALCAN dataset analysis found that ZFP36L1 was significantly upregulated in GBM vs. normal brain tissues, and high ZFP36L1 expression was positively associated with poor survival of GBM patients. Western blot analysis demonstrated that ZFP36L1 was significantly upregulated in seven GBM cell lines vs. NHA. Overexpression of miR-129-5p in LN229 and A172 cells significantly inhibited ZFP36L1 mRNA and protein expression, while overexpression of ZFP36L1 in LN229 and A172 cells reversed miR-129-5p-mediated inhibition on GBM tumorigenesis. Our results revealed an important role of miR-129-5p in the negative regulation of ZFP36L1 expression in GBM, suggesting new candidates for targeted therapy in GBM patients.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
How to Cite
Accepted 2019-11-24
Published 2020-11-02









