WD-3 inhibits the proliferation of breast cancer cells by regulating the glycolytic pathway
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2019.4530Keywords:
Breast cancer, WD-3, glycolysis, hexokinase 2, apoptosis, ATP, antitumor activityAbstract
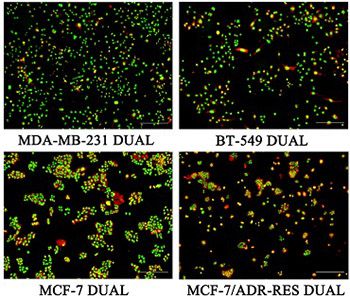
Number 3 Prescription (WD-3) is an herbal remedy used in traditional Chinese medicine that has been shown to improve the outcomes of patients with advanced colon and gastric cancers. This study aimed to investigate the effect of WD-3 on proliferation, glycolysis, and hexokinase 2 expression in breast cancer cells. Four breast cancer cell lines (MDA-MB-231, BT-549, MCF-7, and MCF-7/ADR-RES) were treated with different concentrations of WD-3 compared with blank control (phosphate-buffered saline). Each of the breast cancer cell lines was also divided into WD-3, paclitaxel, and blank control group. Cell proliferation and morphology were assessed by MTT assay, nuclear Hoechst 33258 staining, or immunofluorescence. Apoptosis was analyzed by flow cytometry. High performance liquid chromatography was used for measurement of ATP, ADP, and AMP. Hexokinase 2 expression was analyzed by Western blot and quantitative reverse transcription PCR. WD-3 inhibited proliferation and increased apoptosis in all four breast cancer cell lines, in a dose-dependent manner. ATP and EC (energy charge) were significantly decreased in WD-3-treated BT-549 and MDA-MB-231 cells. WD-3 significantly downregulated the protein and mRNA expression of hexokinase II in BT-549 cells, however, not in the other three breast cancer cell lines. Our findings indicate that WD-3 targets the glycolytic pathway in breast cancer cells to exert its antitumor activity.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
How to Cite
Accepted 2020-01-10
Published 2020-05-01









