Immunohistochemical study of dental pulp cells with 3D collagen type I gel in demineralized dentin tubules in vivo
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2020.4614Keywords:
Collagen type I gel, demineralized dentin tubules, dental pulp cells, osteogenesisAbstract
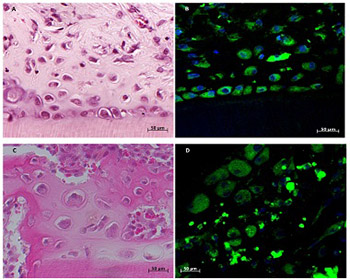
Dental pulp cells (DPCs) represent good candidates for the regeneration of dental tissue. This study aimed to evaluate the growth and differentiation potential of DPCs cultured inside demineralized dentin tubules in vivo. Six green fluorescent protein-transgenic rats (body weight 100 g each) and thirty-two Sprague-Dawley (SD) male rats (body weight 250 g each) were used for DPC collection and dentin tubules preparation and transplantation, respectively. Third-passage DPCs with or without collagen gels were loaded into demineralized dentin tubules. Both types of grafts were transplanted into the rectus abdominis muscles of SD rats and were harvested after 21 days. The expression of alkaline phosphatase (ALP), bone sialoprotein (BSP), osteopontin (OPN), nestin, and dentin sialoprotein (DSP) was analyzed by immunohistochemistry. Histological analysis showed that DPCs in the collagen gel formed an osteodentin-like hard tissue matrix after 21 days. Increased positive immunoreactivity for ALP, BSP, OPN, nestin, and DSP was observed in experimental groups compared with control. Our results demonstrate that DPCs in collagen gel inside demineralized dentin tubules show increased growth and differentiation.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
How to Cite
Accepted 2020-03-27
Published 2020-11-02









