Progress in research on childhood T-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia, Notch1 signaling pathway, and its inhibitors: A review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2020.4687Keywords:
Childhood leukemia, Notch1 signaling pathway, T-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia, T-ALLAbstract
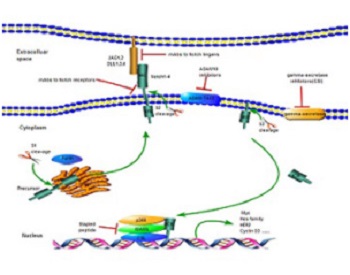
Childhood leukemia is cancer that seriously threatens the life of children in China. Poor sensitivity to chemotherapy and susceptibility to drug resistance are the reasons for the treatment of T-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia (T-ALL) being extremely difficult. Moreover, traditional intensive chemotherapy regimens cause great damage to children. Therefore, it is highly important to search for targeted drugs and develop a precise individualized treatment for child patients. There are activating mutations in the NOTCH1 gene in more than 50% of human T-ALLs and the Notch signaling pathway is involved in the pathogenesis of T-ALL. In this review, we summarize the progress in research on T-ALL and Notch1 signaling pathway inhibitors to provide a theoretical basis for the clinical treatment of T-ALL.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
Accepted 2020-04-25
Published 2021-04-01









