Circ-RNF13, as an oncogene, regulates malignant progression of HBV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma cells and HBV infection through ceRNA pathway of circ-RNF13/miR-424-5p/TGIF2
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2020.5266Keywords:
Circ-RNF13, miR-424-5p, TGIF2, HCC, HBVAbstract
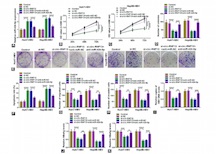
Circular RNA RNF13 (circ-RNF13; ID: hsa_circ_0067717) is newly identified to be abnormally upregulated in hepatitis B virus (HBV)-associated hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients. However, its role and mechanism remain to be further annotated. First of all, real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) was utilized to examine RNA expression, and circ-RNF13 was upregulated in HBV-infected human HCC tissues and HBV-expressing cells (Huh7-HBV and Hep3B-HBV), accompanied with TGFβ-induced factor homeobox 2 (TGIF2) upregulation and microRNA (miR)-424-5p downregulation. Loss-of-functional experiments were performed using MTS assay, colony formation assay, flow cytometry, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, transwell assay, and xenograft tumor model. As a result, blocking circ-RNF13 enhanced the apoptosis rate of Huh7-HBV and Hep3B-HBV cells, but inhibited cell proliferation, colony formation, migration, and invasion in vitro, along with suppressed tumor growth in vivo. Besides, RT-qPCR data showed that HBV DNA copies and levels of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) and hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) were diminished by circ-RNF13 knockdown in Huh7-HBV and Hep3B-HBV cells. Mechanistically, circ-RNF13 and TGIF2 could directly interacting with miR-424-5p according to dual-luciferase reporter assay, suggesting that circ-RNF13 and TGIF2 served as competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) for miR-424-5p. Functionally, overexpressing miR-424-5p mimicked and silencing miR-424-5p counteracted the effects of circ-RNF13 depletion in HBV-expressing HCC cells in vitro; TGIF2 restoration partially abrogated the role of miR-424-5p upregulation. In conclusion, circ-RNF13 might sponge miR-424-5p to suppress HBV-associated HCC cells malignant progression and HBV infection by regulating TGIF2, providing a novel insight into the occurrence and treatment of HBV-associated HCC.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
How to Cite
Accepted 2021-01-29
Published 2021-10-01









