Trends of incidence and prognosis of upper tract urothelial carcinoma
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2020.5345Keywords:
Upper tract urothelial carcinoma, incidence, prognostic nomogram, survival outcome, SEERAbstract
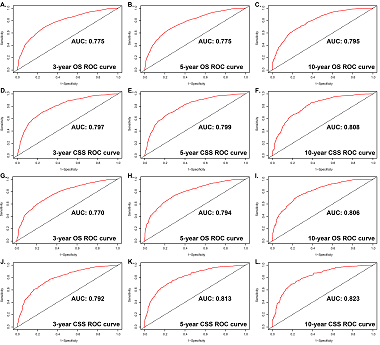
The purpose of this study was to investigate trends in the incidence of upper tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC) in patients and to establish a reliable and practical nomogram based on significant clinical factors to predict the overall survival (OS) and cancer-specific survival (CSS) of UTUC patients. The Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database was used to extract data on UTUC patients between 1988 and 2015. Incidence was calculated using Joinpoint regression software, and trends were quantified by annual percentage change (APC). A nomogram was constructed using R software to predict the OS and CSS probabilities for individual patients. From 1988 to 2015, the incidence of UTUC showed a downward trend (1988: 1.57/100,000 to 2015: 1.51/100,000; APC=-0.1). After stratification according to sex, age and primary site, we found that the incidences of UTUC in males, patients 70+ years old and the renal pelvis were higher than those in females, patients <70 years old and ureter cancer patients. In the training cohort, the nomogram established based on multivariate Cox regression results showed better OS and CSS accuracy (OS: C-index=0.701, AUC=0.736; CSS: C-index=0.729, and AUC=0.688) than SEER stage. In addition, the calibration curves showed good consistency between the predicted and actual 3-, 5- and 10-year OS and CSS rates of the nomogram. In the past 30 years, the incidence of UTUC has shown a general downward trend, and the prognostic nomogram we established can provide a personalized risk assessment for the survival of UTUC patients.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
How to Cite
Accepted 2020-12-14
Published 2021-10-01









