The role of WDR76 protein in human diseases
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2020.5506Keywords:
WD40 repeat, WDR76, ubiquitination, human diseaseAbstract
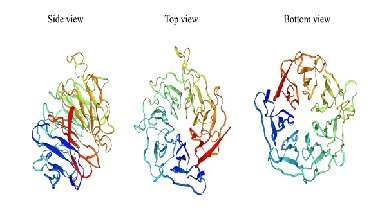
The WD40 repeat (WDR) domain is one of the most abundant protein interaction domains in the human proteome. More than 360 protein interaction domains have been annotated thus far. The WDR domains mediate interactions with peptide regions of important interaction partners in a variety of biological processes. Proteins with the WDR domain which typically contains a seven-bladed β propeller, are continuously being discovered. They represent a large class of proteins that are likely to play important roles. WD40 repeat domain-containing protein 76 (WDR76) is a member of WDR domain-containing proteins. Although it remains poorly understood, it is potentially involved in DNA damage repair, apoptosis, cell cycle progression, and gene expression regulation. Ongoing research on WDR76 is increasing the knowledge regarding its basic functions and role in different pathophysiological. The study of WDR76 is challenging due to the complexity of its interactions with its partners. In the present review, we summarized the current knowledge regarding WDR76, its physiological functions, the close relationship with human diseases, and potential opportunities for target therapy.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
Accepted 2021-03-07
Published 2021-10-01









