Quantitative detection of circulating MT-ND1 as a potential biomarker for colorectal cancer
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2021.5576Keywords:
MT-ND1, colorectal cancer, mtDNA, cfDNA, biomarkerAbstract
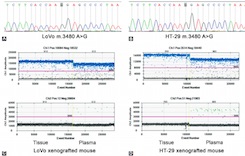
Liquid biopsy represents a diagnostic and monitoring tool and the circulating cell-free mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) plays a vital role in tumor diagnosis and dynamic assessment. Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most common fatal cancers worldwide. Mitochondrially encoded NADH dehydrogenase subunit 1 (MT-ND1) encodes the biggest subunit of respiratory complex I of mtDNA, and mutations in the MT-ND1 are common in CRC. We sought to determine if mutations in circulating MT-ND1 could be a potential biomarker for colorectal cancer. In this study, twenty-two CRC patients at Zhujiang Hospital were included. We mainly used droplet digital PCR to determine the mutation status of MT-ND1, combined with clinical data. In the experiment in vivo, cell-free mtDNA generally presented high concordance with tumor tissues. By quantitative PCR, the MT-ND1 content of plasma in CRC patients was significantly higher than that in healthy individuals (58.01 vs. 0.64, p=0.027). The detection of circulating MT-ND1 content and variants (m.3606 A>G, m.3970 C>T, m.4071 C>T, m.4086 C>T) in cfDNA showed a good correlation with predicted tumor response and progression to chemotherapy. In conclusion, the content and variants of circulating MT-ND1 may become a versatile tool for the diagnosis and monitoring of colorectal cancer.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
Accepted 2021-03-14
Published 2021-10-01









