Development and validation of a ferroptosis-related lncRNAs prognosis signature in colon cancer
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2020.5617Keywords:
TCGA, colon adenocarcinoma, ferroptosis, long non-coding RNA, prognosis signatureAbstract
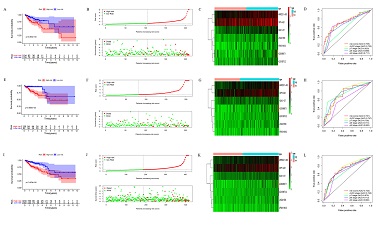
Ferroptosis is a form of iron-dependent programmed cell death. Regulation of ferroptosis in tumor cells is a novel treatment modality. The present study aimed to investigate ferroptosis-related long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and construct a prognostic model for colon adenocarcinoma (COAD). RNA- sequencing data and ferroptosis-related genes were obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas database and FerrDb database. COAD patients were randomly assigned to training- and validation groups. The Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator regression and Cox regression model were used to determine and develop a predictive model. The model was corroborated using the validation group and the entire group. In total, 259 ferroptosis-related genes and 905 ferroptosis-related LncRNAs were obtained. Cox model revealed and constructed seven ferroptosis-related LncRNAs signature (LINC01503, AC004687.1, AC010973.2, AP001189.3, ARRDC1-AS1, OIP5-AS1, and NCK1-DT). Patients were assigned into two groups according to the median risk score. Kaplan–Meier survival curves showed that overall survival between high- and low-risk groups was statistically significant (P<0.01). Cox multivariate analysis seven ferroptosis-related LncRNAs signature was an independent risk factor for COAD outcomes (P<0.05). The relationship between seven ferroptosis-related LncRNAs and clinicopathological features was also examined. The principal component analysis showed a difference between high- and low-risk groups intuitively. With the aid of gene set enrichment analysis, the underlying mechanisms of seven ferroptosis-related LncRNAs were uncovered, including the MAPK signaling pathway, mTOR signaling pathway, and glutathione metabolism pathway. Finally, we established and validated seven ferroptosis-related lncRNAs signature for COAD patients to predict survival. These results may provide meaningful targets for future study.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
How to Cite
Accepted 2021-03-04
Published 2021-10-01









