CircFOXM1 promotes the proliferation, migration, invasion, and glutaminolysis of glioblastoma by regulating the miR-577/E2F5 axis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2021.6028Keywords:
Glioblastoma, circFOXM1, miR-577, E2F5Abstract
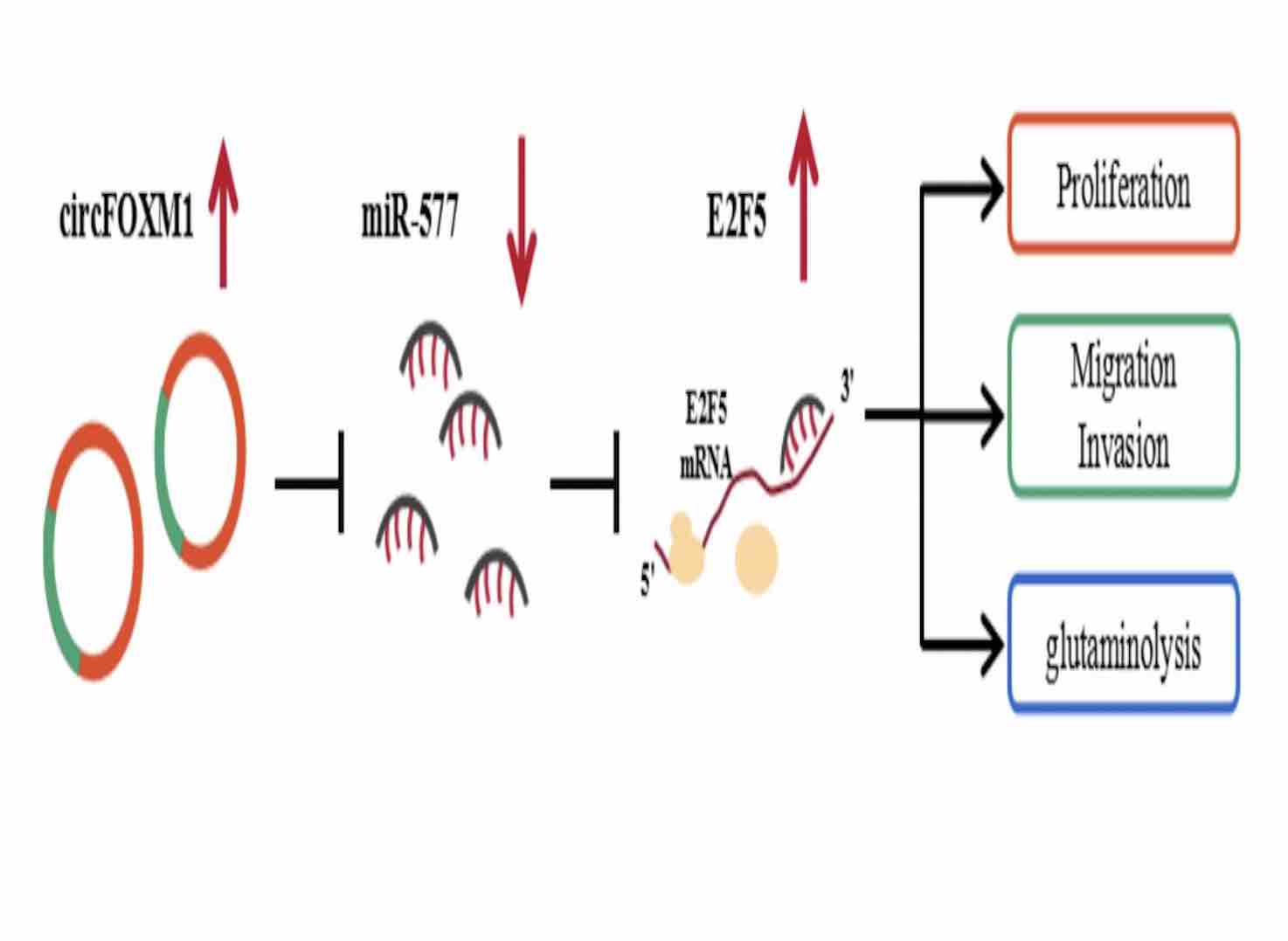
Circular RNA (circRNA) is a key regulator of tumor progression. However, the role of circFOXM1 in glioblastoma (GBM) progression is unclear. The aim of this study was to investigate the role of circFOXM1 in GBM progression. The expression levels of circFOXM1, miR-577, and E2F transcription factor 5 (E2F5) were examined by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Cell counting kit 8 assay, EdU staining, and transwell assay were used to detect cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. The levels of glutamine, glutamate, and α-ketoglutarate were determined to evaluate the glutaminolysis ability of cells. Protein expression was tested by Western blot analysis. Dual-luciferase reporter assay, RNA pull-down assay, and RNA immunoprecipitation assay were employed to verify the interaction between miR-577 and circFOXM1 or E2F5. Mice xenograft model for GBM was constructed to perform in vivo experiments. Our results showed that circFOXM1 was highly expressed in GBM tumor tissues and cells. Silencing of cir FOXM1 inhibited GBM cell proliferation, migration, invasion, glutaminolysis, as well as tumor growth. MiR-577 could be sponged by circFOXM1, and its inhibitor could reverse the suppressive effect of circFOXM1 downregulation on GBM progression. E2F5 was a target of miR-577, and the effect of its knockdown on GBM progression was consistent with that of circFOXM1 silencing. CircFOXM1 positively regulated E2F5 expression, while miR-577 negatively regulated E2F5 expression. In conclusion, our data confirmed that circFOXM1 could serve as a sponge of miR-577 to enhance the progression of GBM by targeting E2F5, which revealed that circFOXM1 might be a biomarker for GBM treatment.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
Accepted 2021-10-02
Published 2022-04-01









