Evaluation of TyG index and TG/HDL-C ratio in HBeAg negative chronic hepatitis B infected patients
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2022.7320Keywords:
TyG index, TG/HDL-C ratio, HBV infection, insulin resistanceAbstract
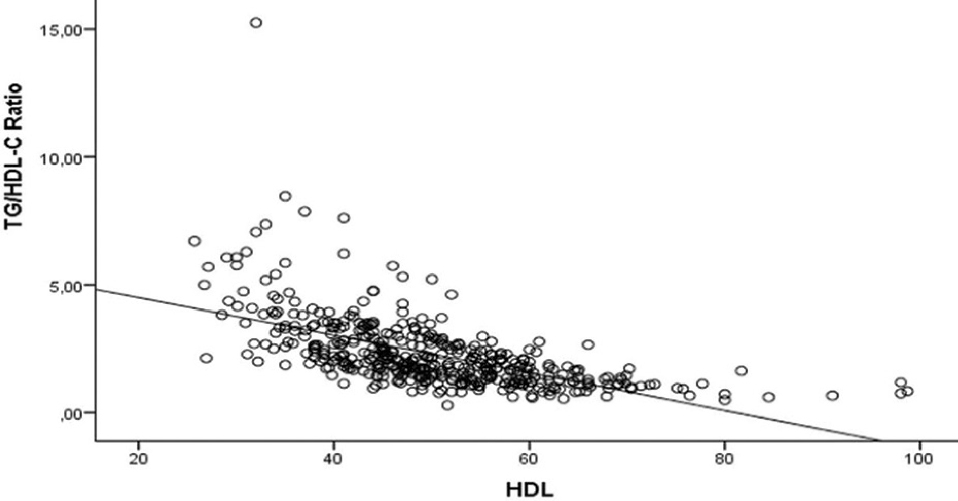
Patients with hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) negative chronic HBV infection are regularly followed up. This study investigates the presence of insulin resistance and the relationship between hepatosteatosis and insulin resistance in patients with HBeAg negative chronic HBV infection using the TyG index and TG/HDL-C ratio. Patients with HBeAg negative chronic HBV infection who applied to the Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology outpatient clinic between January 2019 and December 2020 were included in the study. Glucose, lipid panel, alanine amino transferase (ALT), acetyl amino transferase (AST), body mass index (BMI), TyG index, TG/HDL-C and hepatobiliary ultrasonography (USG) results were evaluated. The data were compared with the control group consisting of 308 HBsAg negative individuals. The study included 132 patients with a median age of 52 years. There was no significant difference between the patient and control groups regarding age, gender and BMI. Glucose, total cholesterol, TG, LDL, AST, ALT, TyG index and TG/HDL-C ratio were significantly higher in patient than in the control group. At the same time, the HDL value was significantly lower in the patients. There was a strong positive correlation between the TG and BMI, and a strong negative correlation between HDL levels and both TyG index and TG/HDL-C ratio. Our findings showed that the TyG index and TG/HDL-C ratio are helpful in the diagnosis of insulin resistance and hepatosteatosis in patients with HBeAg negative chronic HBV infection.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Tülay Ünver ulusoy, Heval Can Bilek, Hacer Demirköse, Ayşegül Keleş

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2022-06-23
Published 2023-01-06









