Urine amylase level after Whipple resection might be a predictive factor of postoperative complications
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2022.7356Keywords:
Urine amylase level, Whipple resection, postoperative complications, postoperative pancreatic fistulaAbstract
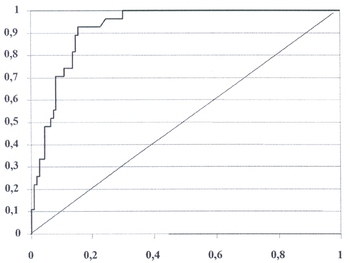
The association between urine amylase levels and the development of postoperative complications after Whipple resection is still unknown. Aim of this study was to determine the prognostic value of urine amylase levels for postoperative complications in patients who underwent Whipple resection. In this retrospective cohort study, we analyzed amylase levels in urine, serum and drains in 52 patients who underwent Whipple resection preoperatively and on Postoperative Day 1 (POD1) after the intervention. Patients were followed up for 3 months to assess their predictive value for postoperative complications. In patients with complications, urine amylase levels were significantly higher on POD1 than before resection (198.89 ± 28.41 vs. 53.70 ± 7.44, p=0.000). Considering the sensitivity and specificity of the urine amylase level on POD1, an area under the ROC curve of 0.918 was obtained (p<0.001, 95% CI: 0.894-0.942). Patients with urine amylase levels ³140.00 U/L had significantly higher risks of postoperative pancreatic fistula (POPF) grade C (definition of POPF done according to the ISGP) (RR:20.26; 95% CI: 1.18-347.07; p=0.038), readmission to hospital (RR: 6.61; 95% CI: 1.53-28.58; p=0.011), reoperation (RR: 5.67; 95% CI: 1.27-25.27; p=0.023), and mortality (RR:17.00; 95% CI: 2.33-123.80; p=0.005) than patients with urine amylase levels <140.00 U/L. Urine amylase levels on POD1 displayed strong and significant positive correlations with serum amylase levels (r=0.92, p=0.001) and amylase levels in drains (r=0.86, p=0.002). We can conclude that urine amylase levels on POD1 have good prognostic value for postoperative complications after Whipple resection and might be used as an additional predictive risk factor.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Farid Ljuca, Amir Tursunović, Kenana Ljuca, Zijah Rifatbegović, Mirha Agić

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2022-05-16
Published 2022-07-29









