Amphiregulin/epidermal growth factor receptor/hypoxia-inducible factor-1α pathway regulates T helper 9 and T cytotoxic 9 cell response in adult patients with infectious mononucleosis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2022.8013Keywords:
infectious mononucleosis, T helper 9 cells, T cytotoxic 9 cells, amphiregulin, growth factor receptor, hypoxia inducible factor-1αAbstract
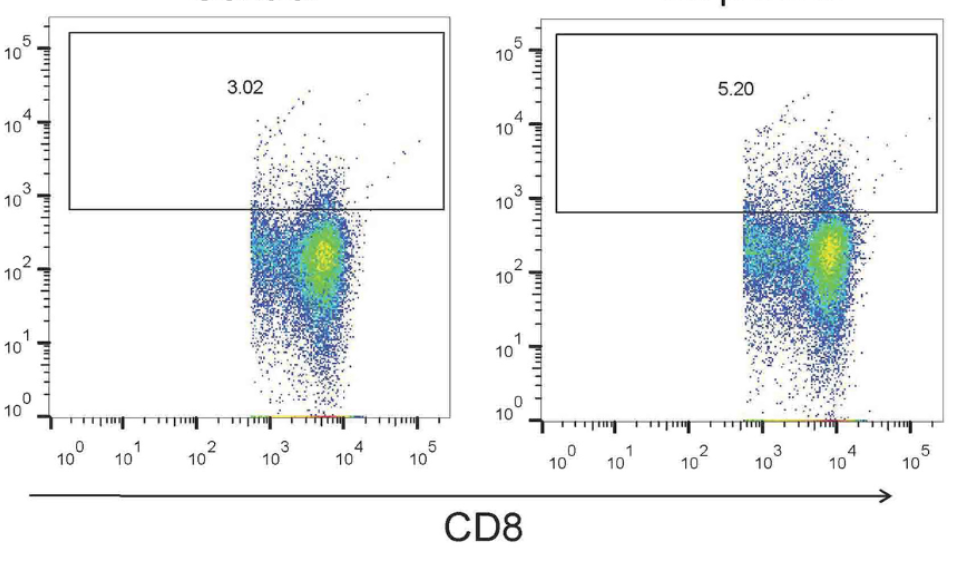
Amphiregulin (AREG)/epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling induces hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α), leading to promotion of T helper 9 (Th9) differentiation and anti-tumor functions. However, the role of the AREG/EGFR/HIF-1α pathway in regulating interleukin-9 (IL-9) production by T cells in adult patients with infectious mononucleosis (IM) has not been fully elucidated. Fifty IM patients and 20 controls were enrolled. The percentages of Th9 and T cytotoxic 9 (Tc9) cells, the mRNA relative expressions of the transcription factors of IL-9-secreting T cells, purine-rich nucleic acid binding protein 1 (PU.1) and forkhead box protein O1 (FOXO1), and the levels of IL-9, AREG, EGFR, and HIF-1α were measured. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells from IM patients were stimulated with EGFR inhibitor or exogenous AREG in the presence or absence of anti-HIF-1α. Regulation of the AREG/EGFR/HIF-1α pathway to IL-9 production by T cells was assessed. The percentages of Th9 and Tc9 cells, plasma IL-9 levels, and PU.1 and FOXO1 mRNA expressions were elevated in IM patients. Plasma levels of AREG and HIF-1α were also increased in IM patients. AREG levels correlated positively with the percentages of Th9 and Tc9 cells in IM patients. Inhibition of EGFR suppressed IL-9-producing T cell differentiation and HIF-1α production. Exogenous AREG stimulation not only induced EGFR and HIF-1α expression but also promoted IL-9-secreting T cell differentiation. Neutralization of HIF-1α abrogated AREG/EGFR-induced Th9 and Tc9 differentiation in IM patients. The current data suggested that the AREG/EGFR/HIF-1α pathway contributed to the elevation of Th9 and Tc9 differentiation in IM patients.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Yu Li, Lan Li, Weihua Zhang, Ying Gao

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2022-09-16
Published 2023-01-06









