Roxadustat: Do we know all the answers?
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2022.8437Keywords:
Erythropoietin, HIF-PHI, roxadustat, renal anemia, therapeutic potentialAbstract
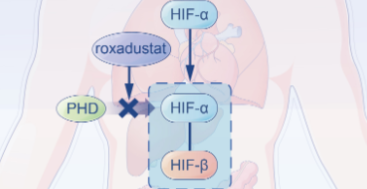
Anemia is a common complication of chronic kidney disease (CKD), and its prevalence rises as the disease progresses. Intravenous or subcutaneous erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) are advised to treat CKD-associated anemia, since shortage of erythropoietin (EPO) and iron are the main cause of anemia. However, ESA resistance and safety have spurred a lot of interest in the development of alternate anemia therapies. Roxadustat, an orally administered hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor (HIF-PHI) that increases erythropoiesis and may modulate iron metabolism, was recently licensed in China, Chile, South Korea, Japan and the European Union for the treatment of CKD-related anemia. Despite this, clinical trials have shown a number of adverse effects, including cardiovascular disease, hyperkalemia, and infections. In addition, of concern is roxadustat's possible effects on other organs and systems. In this review, based on clinical evidence, we discuss the potentially detrimental effects of roxadustat to the known biology on systems other than kidney, and the need for long-term follow-up in order for roxadustat to be approved in more countries in the future.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Qiu-Yu Li, Qian-Wen Xiong, Xuefeng Yao, Fei Liu, Xiaoxiao Tang, Haidong Fu, Tong Tong, Jianhua Mao, Wan-Xin Peng

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2022-12-23
Published 2023-05-01









